Air - Moisture Holding Capacity vs. Temperature
The moisture holding capacity of air increases with temperature.
The moisture holding capacity of air increases dramatically with increased temperature as indicated in the diagrams below.
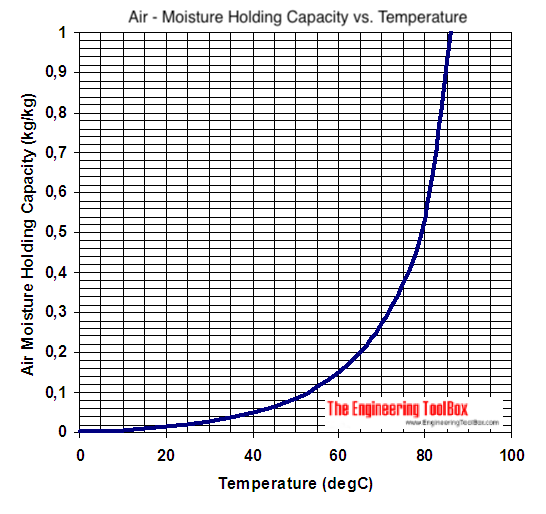
Air Moisture Holding Capacity - SI Units
Moisture holding capacity of air - kg water per kg dry air:
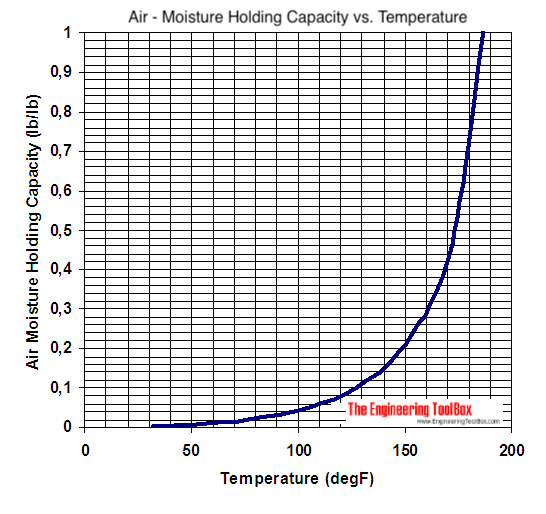
Air Moisture Holding Capacity - Imperial Units
Moisture holding capacity of air - lb water per lb dry air:
Moisture holding capacity of air - lb water per 1000 cubic feet dry air:
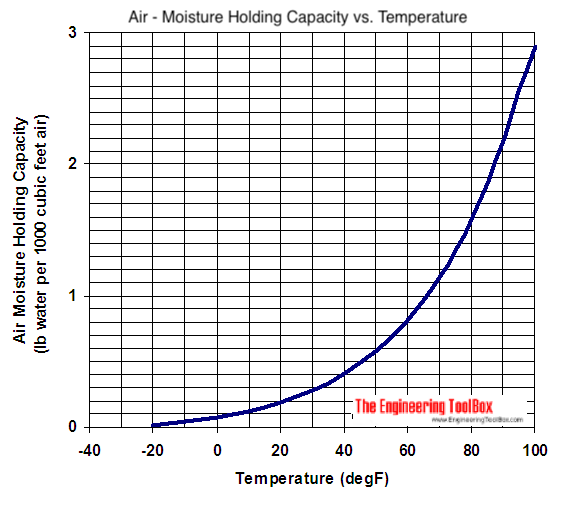
Note - the moisture holding capacity of air at 100 oF (38 oC) is 10 times the moisture holding capacity of air at 30 oF (~ 0 oC). This is a very important observation - especially when working with drying processes where air is used to transport moisture away from process and products.
In general
- it is in general good energy economy to increase the air temperature in a dryer as much as possible! - the increased moisture transport capacity of air at higher temperature out-weights the increased energy-consumption for heating the dry air to higher temperature!



