Removing Heat with Air
Calculating heat removed with air by measuring the wet bulb temperature.
The wet bulb temperature is a measure of the total heat in moist air - the mixture of dry air and vapor.
If the initial and final wet bulb temperatures in a heating or cooling processes are known - the heat transported by the air in the processes can be calculated by using the charts below.
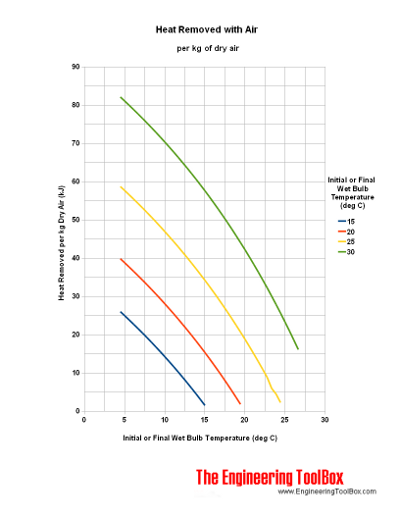
Heat Transported by Air - kJ per kg
Example - Heat Removed by Moist Air
Air with initial wet bulb temperature 30oC (green line) is cooled down to a final temperature 10oC. From the diagram above we can estimate that
aprox. 70 kJ
of heat is removed.