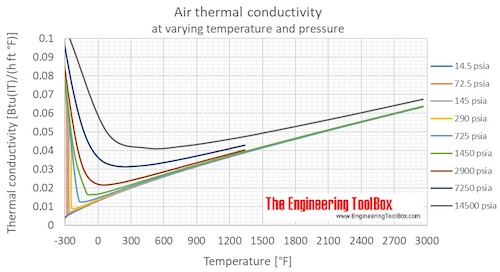
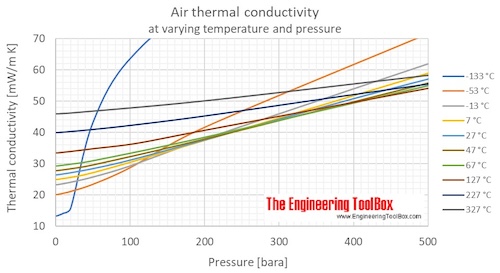
Air Properties - Thermal Conductivity vs. Temperature and Pressure Charts and Calculator
Online calculator with figures and tables showing air thermal conductivity vs. temperature and pressure. SI and imperial units.
Thermal conductivity is a material property that describes ability to conduct heat . Thermal conductivity can be defined as
" the quantity of heat transmitted through a unit thickness of a material - in a direction normal to a surface of unit area - due to a unit temperature gradient under steady state conditions".
Thermal conductivity most common units are W/(m K) in the SI system and Btu/(h ft °F) in the Imperial system.
Tabulated values and thermal conductivity units conversion are given below the figures.
Online Air Thermal Conductivity Calculator
The calculator below can be used to calculate the air thermal conductivity at given temperatures and pressure.
The output conductivity is given as mW/(m K), Btu(IT)/(h ft °F) and kcal(IT)/(h m K).
See also other properties of Air at varying temperature and pressure: Density and specific weight at varying temperature, Density at varying pressure, Diffusion Coefficients for Gases in Air, Prandtl Number, Specific heat at varying temperature and Specific heat at varying pressure, Thermal Diffusivity, Properties at gas-liquid equilibrium conditions and Air thermophysical properties at standard conditions and Composition and molecular weight,
as well as thermal conductivity o f ammonia, butane, carbon dioxide, ethane, ethylene, hydrogen, methane, nitrogen, propane and water.
See also Conductive Heat Transfer Calculator
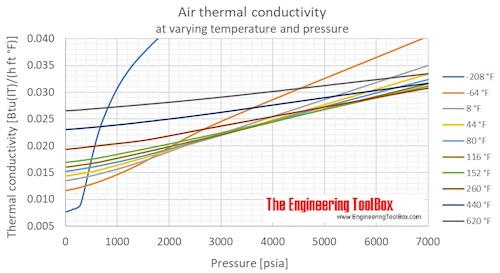
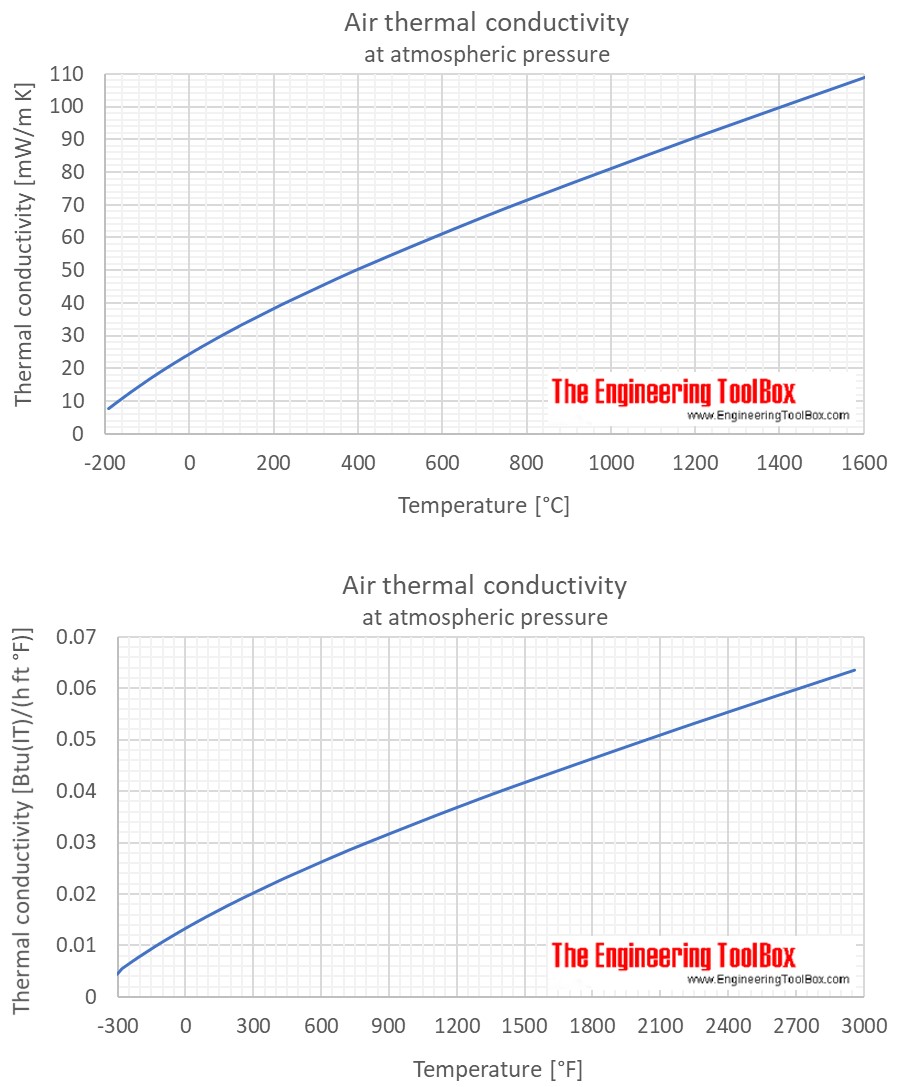
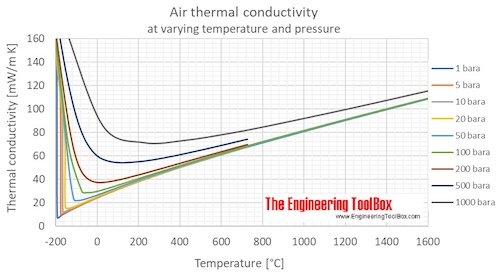
Air thermal conductivity at atmospheric pressure and temperatures given in °C:
| Temperature | Thermal conductivity | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (°C) | (mW/m K) | (kcal(IT)/(h m K)) | (Btu(IT)/(h ft °F)) |
| -190 | 7.82 | 0.00672 | 0.00452 |
| -150 | 11.69 | 0.01005 | 0.00675 |
| -100 | 16.20 | 0.01393 | 0.00936 |
| -75 | 18.34 | 0.01577 | 0.01060 |
| -50 | 20.41 | 0.01755 | 0.01179 |
| -25 | 22.41 | 0.01927 | 0.01295 |
| -15 | 23.20 | 0.01995 | 0.01340 |
| -10 | 23.59 | 0.02028 | 0.01363 |
| -5 | 23.97 | 0.02061 | 0.01385 |
| 0 | 24.36 | 0.02094 | 0.01407 |
| 5 | 24.74 | 0.02127 | 0.01429 |
| 10 | 25.12 | 0.02160 | 0.01451 |
| 15 | 25.50 | 0.02192 | 0.01473 |
| 20 | 25.87 | 0.02225 | 0.01495 |
| 25 | 26.24 | 0.02257 | 0.01516 |
| 30 | 26.62 | 0.02289 | 0.01538 |
| 40 | 27.35 | 0.02352 | 0.01580 |
| 50 | 28.08 | 0.02415 | 0.01623 |
| 60 | 28.80 | 0.02477 | 0.01664 |
| 80 | 30.23 | 0.02599 | 0.01746 |
| 100 | 31.62 | 0.02719 | 0.01827 |
| 125 | 33.33 | 0.02866 | 0.01926 |
| 150 | 35.00 | 0.03010 | 0.02022 |
| 175 | 36.64 | 0.03151 | 0.02117 |
| 200 | 38.25 | 0.03289 | 0.02210 |
| 225 | 39.83 | 0.03425 | 0.02301 |
| 300 | 44.41 | 0.03819 | 0.02566 |
| 412 | 50.92 | 0.04378 | 0.02942 |
| 500 | 55.79 | 0.04797 | 0.03224 |
| 600 | 61.14 | 0.05257 | 0.03533 |
| 700 | 66.32 | 0.05702 | 0.03832 |
| 800 | 71.35 | 0.06135 | 0.04122 |
| 900 | 76.26 | 0.06557 | 0.04406 |
| 1000 | 81.08 | 0.06971 | 0.04685 |
| 1100 | 85.83 | 0.07380 | 0.04959 |
Air thermal conductivity at atmospheric pressure and temperatures given in °F:
| Temperature | Thermal conductivity | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (°F) | (Btu(IT)/(h ft °F)) | (kcal(IT)/(h m K)) | (mW/m K) |
| -300 | 0.00484 | 0.00720 | 8.37 |
| -200 | 0.00788 | 0.01172 | 13.63 |
| -100 | 0.01068 | 0.01589 | 18.48 |
| -50 | 0.01200 | 0.01786 | 20.77 |
| -20 | 0.01277 | 0.01901 | 22.10 |
| 0 | 0.01328 | 0.01976 | 22.98 |
| 10 | 0.01353 | 0.02013 | 23.41 |
| 20 | 0.01378 | 0.02050 | 23.84 |
| 30 | 0.01402 | 0.02087 | 24.27 |
| 40 | 0.01427 | 0.02123 | 24.70 |
| 50 | 0.01451 | 0.02160 | 25.12 |
| 60 | 0.01476 | 0.02196 | 25.54 |
| 70 | 0.01500 | 0.02232 | 25.95 |
| 80 | 0.01524 | 0.02267 | 26.37 |
| 100 | 0.01571 | 0.02338 | 27.19 |
| 120 | 0.01618 | 0.02408 | 28.00 |
| 140 | 0.01664 | 0.02477 | 28.80 |
| 160 | 0.01710 | 0.02545 | 29.60 |
| 180 | 0.01755 | 0.02612 | 30.38 |
| 200 | 0.01800 | 0.02679 | 31.16 |
| 250 | 0.01911 | 0.02843 | 33.07 |
| 300 | 0.02018 | 0.03003 | 34.93 |
| 350 | 0.02123 | 0.03160 | 36.75 |
| 400 | 0.02226 | 0.03313 | 38.53 |
| 450 | 0.02327 | 0.03463 | 40.28 |
| 500 | 0.02426 | 0.03611 | 41.99 |
| 600 | 0.02620 | 0.03898 | 45.34 |
| 700 | 0.02807 | 0.04177 | 48.58 |
| 800 | 0.02990 | 0.04449 | 51.74 |
| 1000 | 0.03342 | 0.04973 | 57.84 |
| 1200 | 0.03680 | 0.05477 | 63.69 |
| 1400 | 0.04007 | 0.05963 | 69.35 |
| 1600 | 0.04325 | 0.06436 | 74.85 |
| 1800 | 0.04635 | 0.06898 | 80.23 |
| 2000 | 0.04941 | 0.07353 | 85.51 |
Thermal conductivity units conversion:
Thermal conductivity unit converter
british thermal unit(international)/(foot hour degree fahrenheit) (Btu(IT)/(ft h°F), british thermal unit(international)/(inch hour degree fahrenheit) (Btu(IT)/(in h°F), british thermal unit(international)*inch/(square foot*hour*degree fahrenheit) ((Btu(IT) in)/(ft² h°F)), kilocalorie/(meter hour degree celcius) (kcal/(m h°C)), joule/(centimeter second degree kelvin) (J/(cm s K)), watt/(meter degree kelvin) (W/(m°C)),
- 1 Btu(IT)/(ft h°F) = 1/12 Btu(IT)/(in h°F) = 0.08333 Btu(IT)/(in h°F) = 12 Btu(IT)in/(ft2h°F) = 1.488 kcal/(m h°C) = 0.01731 J/(cm s K) = 1.731 W/(m K)
- 1 Btu(IT)/(in h°F) = 12 Btu(IT)/(ft h°F) = 144 Btu(IT)in/(ft2h°F) = 17.858 kcal/(m h°C) = 0.20769 J/(cm s K)= 20.769 W/(m K)
- 1 (Btu(IT) in)/(ft² h°F) = 0.08333 Btu(IT)/(ft h°F) = 0.00694 Btu(IT)/(in h°F) = 0.12401 kcal/(m h°C) = 0.001442 J/(cm s K) = 0.1442 W/(m K)
- 1 J/(cm s K) = 100 W/(m K) = 57.789 Btu(IT)/(ft h°F) = 4.8149 Btu(IT)/(in h°F) = 693.35 (Btu(IT) in)/(ft² h°F) = 85.984 kcal/(m h°C)
- 1 kcal/(m h°C) = 0.6720 Btu(IT)/(ft h°F) = 0.05600 Btu(IT)/(in h°F) = 8.0636 (Btu(IT) in)/(ft2h°F) = 0.01163 J/(cm s K) = 1.163 W/(m K)
- 1 W/(m K) = 0.01 J/(cm s K) = 0.5779 Btu(IT)/(ft h°F) = 0.04815 Btu(IT)/(in h°F) = 6.9335 (Btu(IT) in)/(ft² h°F) = 0.85984 kcal/(m h°C)