Water - Ionization Constant, pKw, of Normal and Heavy Water
Ionization constant (= dissociation constant = self-ionization constant = ion product = autoprotolysis constant ) of water and heavy water, given as function of temperature (°C and °F) in figures and tables.
Autoprotolysis describes the reaction of water with itself:
2 H2O ↔ H3 O++ OH¯ (1)
and an equlibrium constant can be defined as
Keq = a(H3 O+) * a(OH-) / a(H2O)2 (2)
where a is the chemical activity of the water ions.
Because most acid–base solutions are typically very dilute, the activity of water is generally approximated as being equal to unity. In dilute aqueous solutions, the activities of the solute particles are approximately equal to their concentrations.
Then, and an autoprotolysis constant or water ionization constant can be defined as
Kw = (H3 O+) (OH¯) (3)
where (H3 O+) and (OH¯) represents the concentration of H3 O+and OH-ions in water.
Often, a general value of 1.00×10¯14 is used. However, pKw varies with the temperature as shown in the figures and tables below.
From the chemical equation (1) above, it can be seen that H3 O+and OH¯ concentrations are in the molar ratio of one-to-one. This means that (H3 O+) = (OH¯). Therefore the values of (H3 O+) and (OH¯) can be determined by taking the square root of Kw .
Heavy water, D2O, self-ionizes less than normal water, which gives larger pKw values for D2O compared to H2O.
See Water and Heavy Water for thermodynamic properties at standard condtions.
See also other properties of Water at varying temperature and pressure : Boiling points at high pressure, Boiling points at vacuum pressure, Density and specific weight, Dynamic and kinematic viscosity, Enthalpy and entropy, Heat of vaporization, Melting points at high pressure, Prandtl number, Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions, Saturation pressure, Specific gravity, Specific heat (heat capacity), Specific volume, Thermal conductivity, Thermal diffusivity and Vapour pressure at gas-liquid equilibrium.
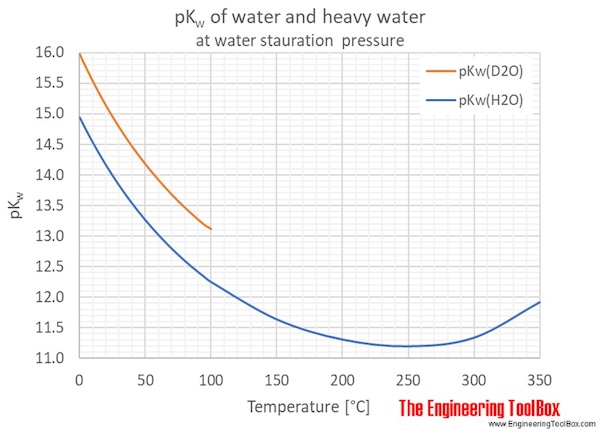
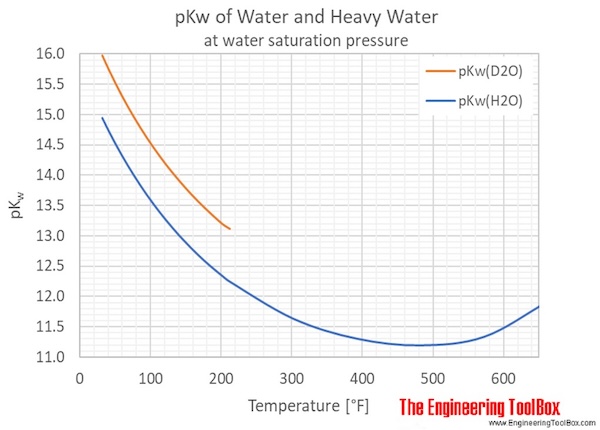
| Temperature | Ionization constant, pKw | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (°C) | (°F) | H2O | D2O |
| 0 | 32 | 14.947 | 15.972 |
| 5 | 41 | 14.734 | 15.743 |
| 10 | 50 | 14.534 | 15.527 |
| 15 | 59 | 14.344 | 15.324 |
| 20 | 68 | 14.165 | 15.132 |
| 25 | 77 | 13.995 | 14.951 |
| 30 | 86 | 13.833 | 14.779 |
| 35 | 95 | 13.680 | 14.616 |
| 40 | 104 | 13.535 | 14.462 |
| 45 | 113 | 13.396 | 14.316 |
| 50 | 122 | 13.265 | 14.176 |
| 55 | 131 | 13.140 | 14.044 |
| 60 | 140 | 13.020 | 13.918 |
| 65 | 149 | 12.907 | 13.798 |
| 70 | 158 | 12.799 | 13.683 |
| 75 | 167 | 12.696 | 13.574 |
| 80 | 176 | 12.598 | 13.470 |
| 85 | 185 | 12.505 | 13.371 |
| 90 | 194 | 12.417 | 13.276 |
| 95 | 203 | 12.332 | 13.186 |
| 100 | 212 | 12.252 | 13.120 |
| 150 | 302 | 11.64 | |
| 200 | 393 | 11.31 | |
| 250 | 482 | 11.20 | |
| 300 | 572 | 11.34 | |
| 350 | 662 | 11.92 | |
| Temperature | Ionization constant, pKw | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (°F) | (°C) | H2O | D2O |
| 32 | 0.0 | 14.947 | 15.972 |
| 40 | 4.4 | 14.758 | 15.768 |
| 50 | 10.0 | 14.534 | 15.528 |
| 60 | 15.6 | 14.324 | 15.302 |
| 70 | 21.1 | 14.126 | 15.090 |
| 80 | 26.7 | 13.940 | 14.891 |
| 90 | 32.2 | 13.764 | 14.705 |
| 100 | 37.8 | 13.598 | 14.529 |
| 110 | 43.3 | 13.442 | 14.364 |
| 120 | 48.9 | 13.293 | 14.208 |
| 130 | 54.4 | 13.153 | 14.060 |
| 140 | 60.0 | 13.020 | 13.918 |
| 150 | 65.6 | 12.895 | 13.785 |
| 160 | 71.1 | 12.776 | 13.658 |
| 170 | 76.7 | 12.663 | 13.537 |
| 180 | 82.2 | 12.556 | 13.423 |
| 190 | 87.8 | 12.455 | 13.317 |
| 200 | 93.3 | 12.360 | 13.219 |
| 210 | 98.9 | 12.270 | 13.13 |
| 212 | 100.0 | 12.252 | 13.12 |
| 250 | 121.1 | 11.97 | |
| 300 | 148.9 | 11.65 | |
| 400 | 204.4 | 11.29 | |
| 500 | 260.0 | 11.20 | |
| 600 | 315.6 | 11.49 | |
| 650 | 343.3 | 11.84 | |



