Melting points of Hydrocarbons, Alcohols and Acids
Melting temperature (°C and °F) with carbon number up to C33.
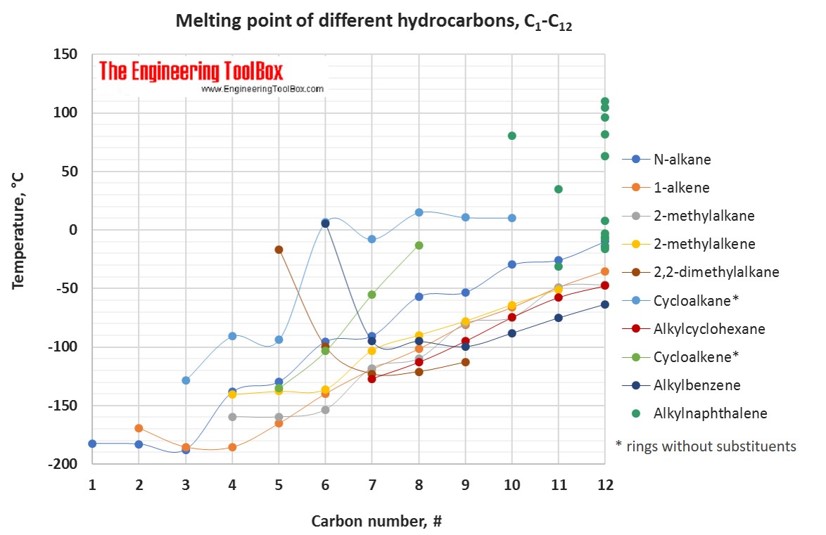
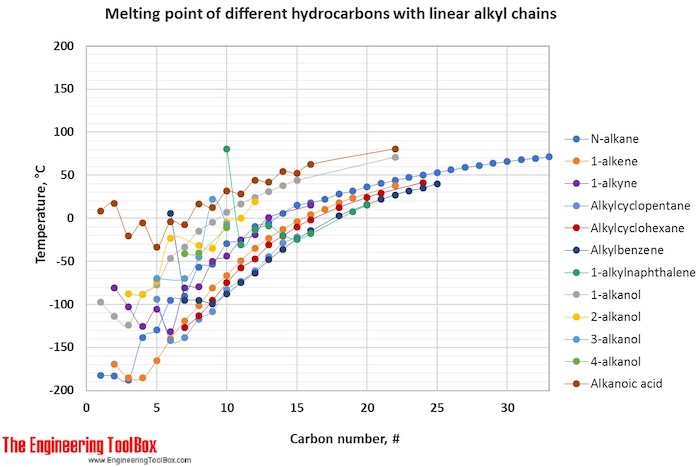
The tables and figures below show how the melting point changes with increasing carbon number up to C33 for different kinds of hydrocarbons, alcohols and carboxylic acids. More detailed definitions and examples of molecular structures of the different classes of organic compounds are given below the figures.
- Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid
- Boiling point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas
For hydrocarbons with the same carbon number the boiling point increases in the following order:
multisubstituted alkane < singelsubstituted alkane < singelsubstituted alkene < normal alkene < normal alkane < alkyl cyclohexane < alkylbenzene < cycloalkene < cycloalkane < 2-, 4- and 3-alkanol / 1-alkylnaphthalene < 1-alkanol < normal alkanoic acid
For melting points, the trends are more varying with increasing carbon number for the different types of hydrocarbons.
See also boiling points of hydrcarbons, alcohols and acids, densities for different kinds of organic compounds and density, boiling and melting points of nitrogen and sulfur compounds.
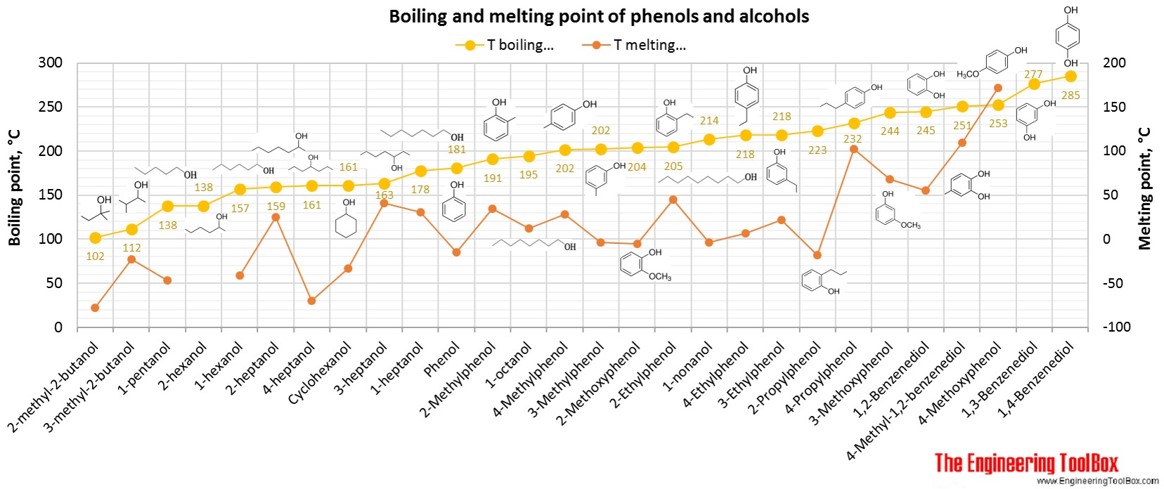
See also pKa values for phenols, alcohols and carboxylic acids.

For full table - rotate the screen!
| Carbon number | Melting point of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids, C1-C16, given in °C | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
| Alkylcyclohexane* | -127 | -113 | -95 | -78 | -58 | -48 | -31 | -20 | -10 | -2 | ||||||
| 2,2-dimetylalkane | -17 | -100 | -123 | -121 | -113 | |||||||||||
| 3-methylalkane | -118 | -119 | -121 | -108 | -85 | -80 | -58 | |||||||||
| Alkylbenzene* | 6 | -95 | -95 | -100 | -88 | -75 | -63 | -48 | -36 | -24 | -14 | |||||
| Alkylcyclopentane | -142 | -138 | -117 | -108 | -83 | -73 | -61 | -45 | -29 | -22 | ||||||
| 2-methylalkane | -160 | -160 | -154 | -118 | -110 | -80 | -75 | -49 | -47 | |||||||
| 1-alkene | -169 | -185 | -185 | -165 | -140 | -119 | -102 | -81 | -66 | -49 | -35 | -23 | -13 | -4 |
4 |
|
| 2-methylalkene | -140 | -138 | -136 | -103 | -90 | -78 | -64 | -51 | ||||||||
| N-alkane | -183 | -183 | -188 | -138 | -130 | -95 | -91 | -57 | -53 | -30 | -26 | -10 | ||||
| 1-alkyne | -81 | -103 | -126 | -106 | -132 | -81 | -79 | -50 | -44 | -25 | -19 | 1 | 15 | |||
| 3-alkanol | -70 | -70 | -45 | 22 | -8 | |||||||||||
| Cycloalkene** | -135 | -104 | -55 | |||||||||||||
| 4-alkanol | -41 | -41 | -11 | |||||||||||||
| 2-alkanol | -88 | -88 | -73 | -23 | -32 | -35 | -5 | 0 | 19 | |||||||
| 1-alkanol | -98 | -114 | -124 | -89 | -78 | -46 | -33 | -15 | -5 | 7 | 17 | 24 | 31 | 38 | 44 | |
| Cycloalkane** | -129 | -91 | -94 | 7 | -8 | 15 | 11 | 10 | ||||||||
| Alkanoic acid | 8 | 17 | -21 | -5 | -34 | -4 | -7 | 17 | 12 | 31 | 29 | 44 | 42 | 63 | ||
| 1-alkylnaphthalene | 80 | -31 | -14 | -9 | -20 | -25 | -18 | |||||||||
| Carbon number | Melting point of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids, C1-C16, given in °F | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
| Alkylcyclohexane* | -197 | -171 | -139 | -108 | -72 | -54 | -24 | -5 | 14 | 29 | ||||||
| 2,2-dimetylalkane | 2 | -148 | -189 | -186 | -171 | |||||||||||
| 3-methylalkane | -180 | -182 | -186 | -162 | -121 | -112 | -72 | |||||||||
| Alkylbenzene* | 42 | -139 | -139 | -147 | -126 | -103 | -82 | -54 | -33 | -11 | 6 | |||||
| Alkylcyclopentane | -224 | -217 | -179 | -162 | -117 | -99 | -78 | -48 | -20 | -8 | ||||||
| 2-methylalkane | -255 | -256 | -245 | -180 | -166 | -112 | -103 | -56 | -53 | |||||||
| 1-alkene | -273 | -302 | -302 | -265 | -220 | -182 | -151 | -114 | -87 | -56 | -31 | -10 | 9 | 25 | 40 | |
| 2-methylalkene | -221 | -216 | -213 | -153 | -130 | -108 | -83 | -60 | ||||||||
| N-alkane | -297 | -297 | -306 | -217 | -201 | -140 | -131 | -70 | -64 | -21 | -14 | 15 | ||||
| 1-alkyne | -113 | -153 | -194 | -158 | -205 | -114 | -111 | -58 | -47 | -13 | -2 | 34 | 59 | |||
| 3-alkanol | -94 | -94 | -49 | 72 | 19 | |||||||||||
| Cycloalkene** | -211 | -154 | -67 | |||||||||||||
| 4-alkanol | -42 | -41 | 12 | |||||||||||||
| 2-alkanol | -126 | -127 | -99 | -9 | -25 | -31 | 23 | 32 | 66 | |||||||
| 1-alkanol | -144 | -173 | -192 | -127 | -108 | -52 | -28 | 6 | 23 | 45 | 62 | 76 | 88 | 100 | 111 | |
| Cycloalkane** | -199 | -131 | -137 | 44 | 18 | 59 | 51 | 51 | ||||||||
| Alkanoic acid | 47 | 63 | -5 | 23 | -28 | 25 | 19 | 62 | 54 | 89 | 83 | 111 | 107 | 145 | ||
| 1-alkylnaphthalene | 177 | -24 | 7 | 17 | -3 | -12 | 0 | |||||||||
| * C#(N-alkyl)=0-10 | ||||||||||||||||
| ** rings without substituents | ||||||||||||||||
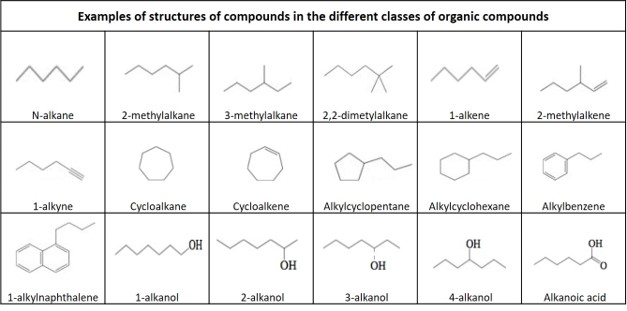
Definitions of organic compounds
Hydrocarbon: An organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon.
Main groups of hydrocarbons:
Alkane: An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula Cn H2n+2 . Also called paraffin .
Alkene: An unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond, with the general formula Cn H2n . Also called olefine .
Alkyne : An unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond, with the general formula Cn H2n-2 . Also called acetylene .
Cycloalkane: A one-ring (monocyclic) saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula Cn H2n . Also called naphthene .
Cycloalkene: An alkene hydrocarbon which contains a closed ring of carbon atoms, but has no aromatic character, with the general formula Cn H2n-2 . Also called cycloolefin .
Aromatic hydrocarbon : A cyclic (ring-shaped), planar (flat) molecule with a ring of resonance bonds that exhibits more stability than other geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms. The simplest of the aromatics have 6 carbon atoms and contains 3 double bounds. A one ring aromatic without any substituents is called benzene, with the formula C6 H6.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons : hydrocarbon that are composed of multiple aromatic rings. A two ring aromatic without any substituents is called naphthalene, with the formula C10 H8 .
Some under-groups of hydrocarbons given in this document:
Alkyl: An alkane substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula Cn H2n+1
2-Methylalkane: A branched alkane, with a methyl group connected to the second carbon atom in the main carbon chain.
3-Methylalkane: A branched alkane, with a methyl group connected to the third carbon atom in the main carbon chain.
2-Methylalkene: A branched alkene, with a methyl group connected to the second carbon atom in the main carbon chain.
Alkylcycklohexane: A monosubstituted cyclohexane with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of the cyclohexane ring, with the general formula Cn H(2n+1) C6 H11 .
Alkylcycklopentane : A monosubstituted cyclopentane with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of the cyclohexane ring, with the general formula Cn H2n+1 C5 H9 .
Alkylbenzene: A monosubstituted benzene with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of the benzene ring, with the general formula Cn H(2n+1) C6 H5.
Alkylnaphthalene: A monosubstituted naphthalene with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of one of the aromatic rings, with the general formula Cn H(2n+1) C10 H7 .
Some other groups of organic compounds:
Alcohol: an organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom
Alkanol: An alcohol where the hydroxyl group is connected to an alkane
Carboxylic acid: an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group (C(=O)OH). The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R–COOH, with R referring to the rest of the molecule.
Alkanoic acid: A carboxylic acid where the R is an alkane.



