Organic Nitrogen Compounds - Physical Data
Boiling and melting points of amines, diamines, pyrroles, pyridines, piperidines and quinolines shown together with their molecular structures, as well as molweights and density.
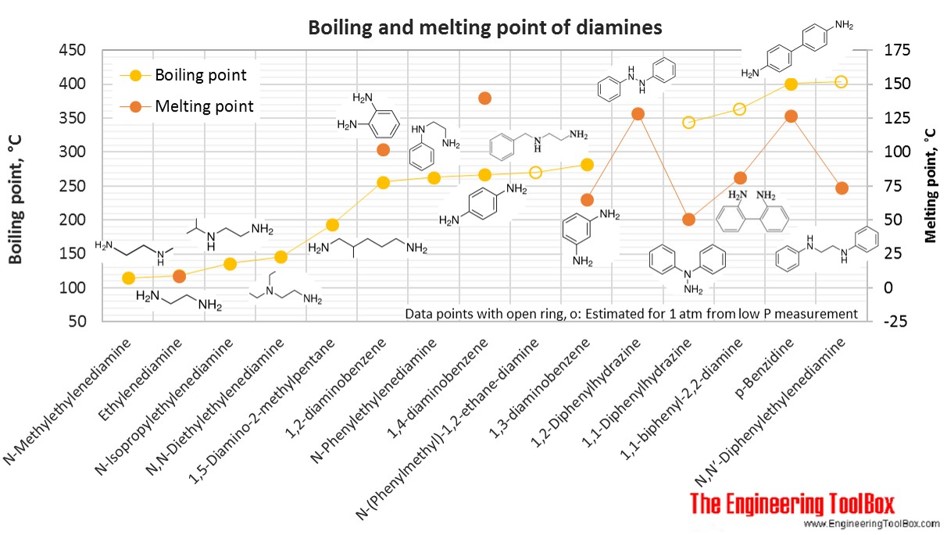
The figures below show the boiling and melting point for organic nitrogen compounds as amines, diamines, pyrroles, pyridines, piperidines and quinolines, together with the molecular structures of the different compounds. The table shows the same numbers together with the molecular weight and density, as well as the numbers of carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen atoms in the molecules. All numbers are given for boiling and melting at 1 atm (760 mm Hg). For some compounds the boiling point at 1 atm is not available. For these, the 1 atm boiling point is estimated from low pressure measurements, using a vaporization heat of 54- 70 kJ/mol (increasing with increasing BP). It is not known whether these compounds are stable at the 1 atm boiling temperature or not. Definitions of the different organic classes are given below the figures.
- Boiling point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas
- Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid
See also similar figures and tables for organic sulfur compounds and boiling and melting point of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids, as well as densities of organic sulfur compounds and pKa of amines, diamines and cyclic organic nitrogen compounds
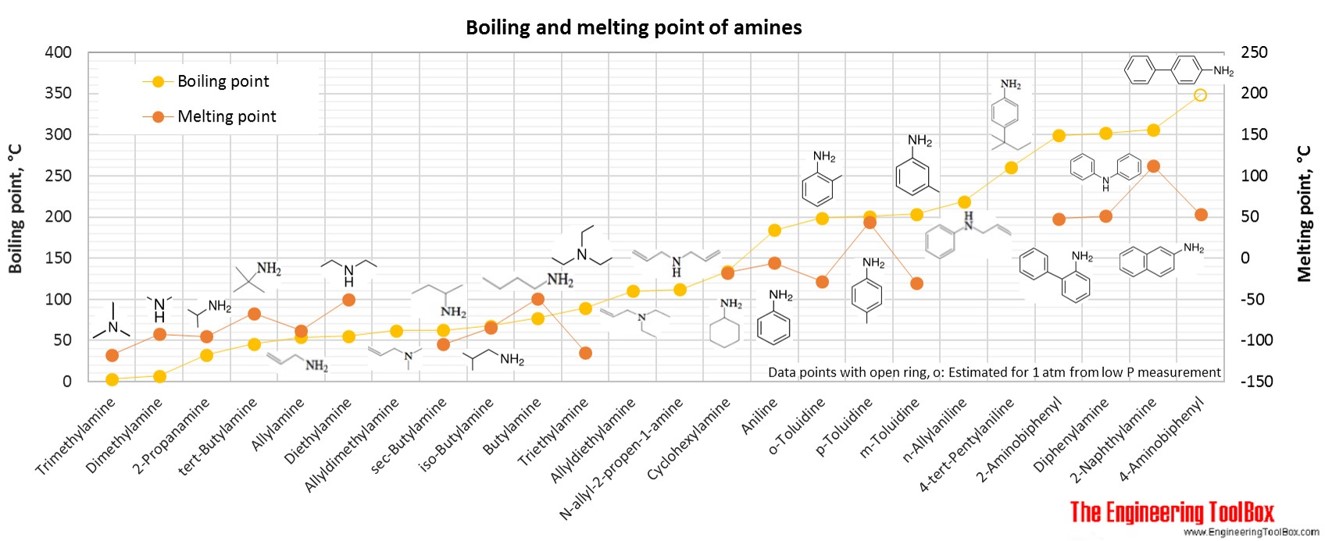
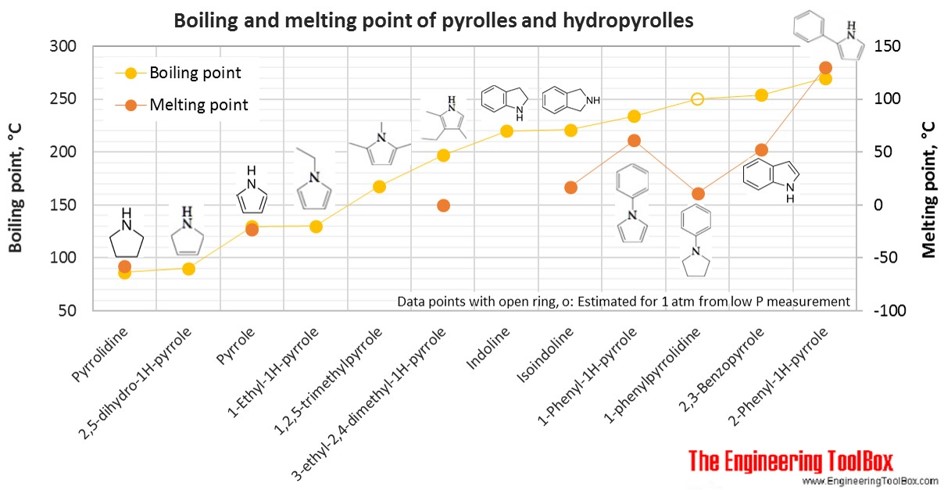
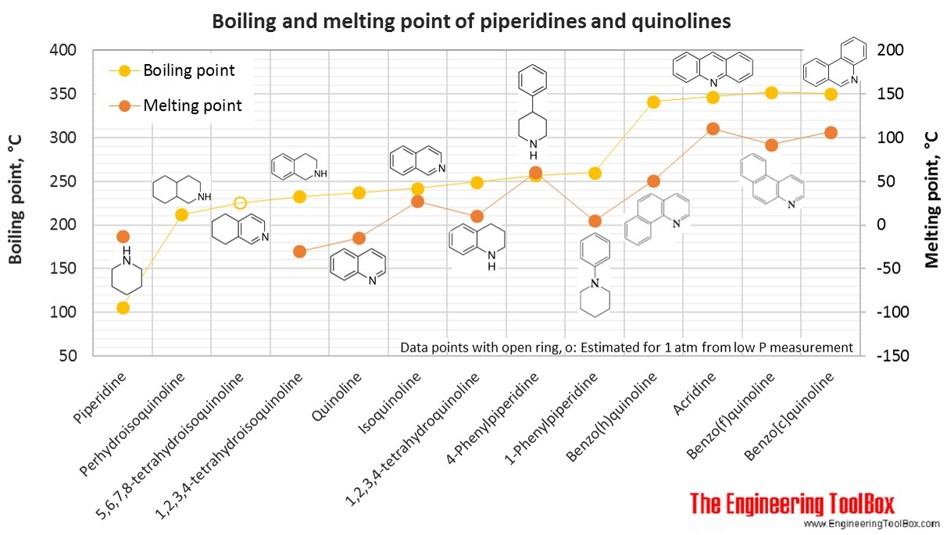
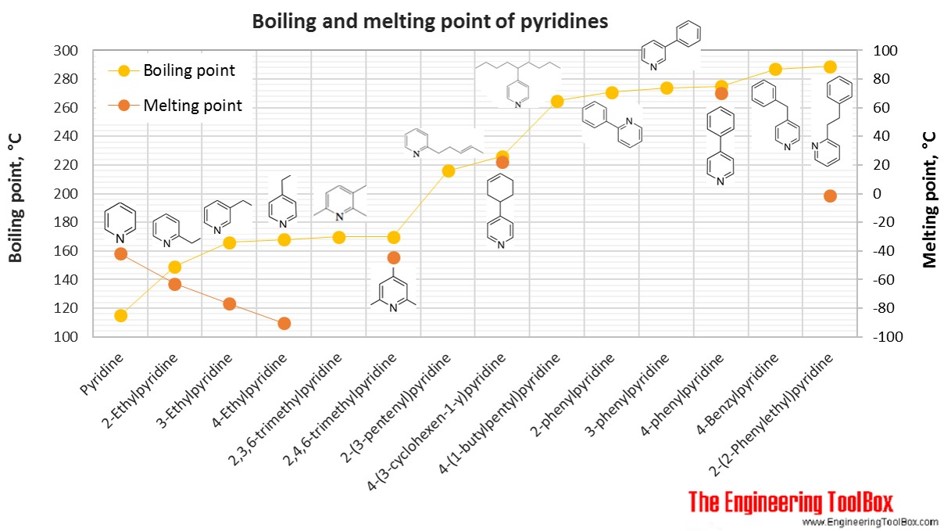
For full table - rotate the screen!
| Group | Compound name | Common name | #C | #H | #N | Molweight (g/mol) | Melting point (°C) | Boiling point (°C) | Density@20°C (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Amine | Methylamine | Methanamine | 1 | 5 | 1 | 31.06 | -93 | -6 | 0.660 |
| 1-Amine | Ethylamine | Ethanamine | 2 | 7 | 1 | 45.08 | -81 | 17 | 0.685 |
| 1-Amine | Propylamine | 1-Propanamine | 3 | 9 | 1 | 59.11 | -85 | 47 | 0.717 |
| 1-Amine | Butylamine | 1-Butanamine | 4 | 11 | 1 | 73.14 | -49 | 77 | 0.741 |
| 1-Amine | Pentylamine | Amylamine | 5 | 13 | 1 | 87.16 | -51 | 105 | 0.754 |
| 1-Amine | Hexylamine | 1-Hexanamine | 6 | 15 | 1 | 101.19 | -21 | 132 | 0.766 |
| 1-Amine | Heptylamine | 1-Heptanamine | 7 | 17 | 1 | 115.22 | -23 | 153 | 0.775 |
| 1-Amine | Octylamine | 1-Octanamine | 8 | 19 | 1 | 129.24 | 0 | 179 | 0.783 |
| 1-Amine | Nonylamine | 1-Nonanamine | 9 | 21 | 1 | 143.27 | -1 | 198 | 0.791 |
| 1-Amine | Decylamine | 1-Decanamine | 10 | 23 | 1 | 157.30 | 15 | 217 | 0.794 |
| 1-Amine | Undecylamine | 1-Undecanamine | 11 | 25 | 1 | 171.32 | 15 | 229 | 0.798 |
| 1-Amine | Dodecylamine | 1-Dodecanamine | 12 | 27 | 1 | 185.35 | 28 | 255 | 0.802 |
| 1-Amine | (Tridecyl)amine | 1-Tridecanamine | 13 | 29 | 1 | 199.38 | 27 | 273 | 0.806 |
| 1-Amine | Tetradecylamine | 1-Tetradecanamine | 14 | 31 | 1 | 213.40 | 39 | 289 | 0.808 |
| 1-Amine | Pentadecylamine | Pentadecanamine | 15 | 33 | 1 | 227.43 | 37 | 312 | 0.810 |
| 1-Amine | Hexadecylamine | 1-Hexadecanamine | 16 | 35 | 1 | 241.46 | 46 | 321 | 0.813 |
| 1-Amine | Octadecylamine | 1-Octadecanamine | 18 | 39 | 1 | 269.51 | 53 | 350 | 0.862 |
| 1-Amine | Icosylamine | 1-Eicosanamine | 20 | 43 | 1 | 297.56 | 389 | ||
| Amine | Dimethylamine | Methyl methylamine | 2 | 7 | 1 | 45.08 | -92 | 7 | 0.654 |
| Amine | Allylamine | 2-propen-1-amine | 3 | 7 | 1 | 57.09 | -88 | 54 | 0.758 |
| Amine | Trimethylamine | Dimethyl methylamine | 3 | 9 | 1 | 59.11 | -117 | 3 | 0.631 |
| Amine | 2-Propanamine | 3 | 9 | 1 | 59.11 | -95 | 32 | 0.682 | |
| Amine | tert-Butylamine | 2-Methyl-2-propanamine | 4 | 11 | 1 | 73.14 | -67 | 46 | 0.696 |
| Amine | Diethylamine | Ethyl ethylamine | 4 | 11 | 1 | 73.14 | -50 | 56 | 0.706 |
| Amine | sec-Butylamine | 2-Butanamine | 4 | 11 | 1 | 73.14 | -105 | 63 | 0.725 |
| Amine | Butylamine | 1-Butanamine | 4 | 11 | 1 | 73.14 | -49 | 77 | 0.741 |
| Amine | iso-Butylamine | 2-Methyl-1-propanamine | 5 | 12 | 1 | 86.16 | -85 | 68 | 0.730 |
| Amine | Aniline | 6 | 7 | 1 | 93.13 | -6 | 184 | 1.025 | |
| Amine | N-allyl-2-propen-1-amine | Diallylamine | 6 | 11 | 1 | 97.16 | 112 | ||
| Amine | Cyclohexylamine | 6 | 13 | 1 | 99.17 | -18 | 134 | 0.819 | |
| Amine | Triethylamine | Diethyl ethylamine | 6 | 15 | 1 | 101.19 | -115 | 90 | 0.727 |
| Amine | o-Toluidine | 2-Aminotoluene, 2-Methylaniline | 7 | 9 | 1 | 107.15 | -28 | 199 | 1.010 |
| Amine | p-Toluidine | 4-Aminotoluene, 4-Methylaniline | 7 | 9 | 1 | 107.15 | 44 | 201 | 0.975 |
| Amine | m-Toluidine | 3-Aminotoluene, 3-Methylaniline | 7 | 9 | 1 | 107.15 | -30 | 203 | 1.001 |
| Amine | Allyldimethylamine | N,N-dimethyl-2-propen-1-amine | 7 | 15 | 1 | 113.20 | 62 | 0.713 | |
| Amine | Allyldiethylamine | N,N-diethyl-2-propen-1-amine | 7 | 15 | 1 | 113.20 | 110 | 0.752 | |
| Amine | n-Allylaniline | Allylphenylamine | 9 | 11 | 1 | 133.19 | 219 | 0.977 | |
| Amine | 2-Naphthylamine | 2-Aminonaphthalene | 10 | 9 | 1 | 143.19 | 112 | 306 | 1.063 |
| Amine | 4-tert-Pentylaniline | 11 | 17 | 1 | 163.26 | 261 | |||
| Amine | 2-Aminobiphenyl | 2-Biphenylylamine, 2-Phenylaniline | 12 | 11 | 1 | 169.22 | 48 | 299 | |
| Amine | Diphenylamine | N-phenyl-aminobenzene | 12 | 11 | 1 | 169.22 | 51 | 302 | 1.160 |
| Amine | 4-Aminobiphenyl | 4-Phenylaniline, Xenylamine | 12 | 11 | 1 | 169.22 | 53 | 348* | |
| Amine | Alverine | N-ethyl-bis(3-phenylpropyl)-amine | 20 | 27 | 1 | 281.44 | 470* | ||
| Pyrrole | Pyrrole | Imidole | 4 | 5 | 1 | 67.09 | -23 | 130 | 0.970 |
| Pyrrole | 2,5-Dihydro-1H-pyrrole | Pyrrolines | 4 | 7 | 1 | 69.11 | 90 | 0.910 | |
| Pyrrole | Pyrrolidine | Azacyclopentane, Tetrahydropyrrole | 4 | 9 | 1 | 71.12 | -58 | 87 | 0.859 |
| Pyrrole | 1-Ethyl-1H-pyrrole | 6 | 9 | 1 | 95.14 | 130 | 0.901 | ||
| Pyrrole | 1,2,5-Trimethylpyrrole | 7 | 11 | 1 | 109.17 | 168 | 0.810 | ||
| Pyrrole | 2,3-Benzopyrrole | 1H-Indole | 8 | 7 | 1 | 117.15 | 52 | 254 | 1.222 |
| Pyrrole | Indoline | 2,3-Dihydroindole, 1-Azaindan | 8 | 9 | 1 | 119.16 | 220 | 1.065 | |
| Pyrrole | Isoindoline | 8 | 9 | 1 | 119.16 | 17 | 221 | 1.052 | |
| Pyrrole | 3-Ethyl-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole | 8 | 13 | 1 | 123.20 | 0 | 197 | 0.913 | |
| Pyrrole | 1-Phenyl-1H-pyrrole | 10 | 9 | 1 | 143.19 | 61 | 234 | ||
| Pyrrole | 2-Phenyl-1H-pyrrole | 10 | 9 | 1 | 143.19 | 130 | 270 | ||
| Pyrrole | 1-phenylpyrrolidine | 10 | 13 | 1 | 147.22 | 11 | 250* | 1.018 | |
| Pyridine | Pyridine | 5 | 5 | 1 | 79.10 | -42 | 115 | 0.982 | |
| Pyridine | 2-Ethylpyridine | 7 | 9 | 1 | 107.15 | -63 | 149 | 0.952 | |
| Pyridine | 3-Ethylpyridine | 7 | 9 | 1 | 107.15 | -77 | 166 | 0.956 | |
| Pyridine | 4-Ethylpyridine | 7 | 9 | 1 | 107.15 | -91 | 168 | 0.942 | |
| Pyridine | 2,3,6-trimethylpyridine | 2,3,6-Collidine | 8 | 11 | 1 | 121.18 | 170 | 0.924 | |
| Pyridine | 2,4,6-trimethylpyridine | 2,4,6-Collidine | 8 | 11 | 1 | 121.18 | -44 | 170 | 0.917 |
| Pyridine | 2-(3-pentenyl)pyridine | 10 | 13 | 1 | 147.22 | 216 | 0.925 | ||
| Pyridine | 2-phenylpyridine | 11 | 9 | 1 | 155.20 | 271 | 1.085 | ||
| Pyridine | 3-phenylpyridine | 11 | 9 | 1 | 155.20 | 274 | 1.084 | ||
| Pyridine | 4-phenylpyridine | 11 | 9 | 1 | 155.20 | 70 | 275 | ||
| Pyridine | 4-(3-cyclohexen-1-y)pyridine | 11 | 13 | 1 | 159.23 | 22 | 226 | 1.024 | |
| Pyridine | 4-Benzylpyridine | 12 | 11 | 1 | 169.22 | 287 | 1.063 | ||
| Pyridine | 2-(2-Phenylethyl)pyridine | 13 | 13 | 1 | 183.25 | -2 | 289 | 1.039 | |
| Pyridine | 4-(1-butylpentyl)pyridine | 14 | 23 | 1 | 205.34 | 265 | 0.890 | ||
| Piperidine | Piperidine | 5 | 11 | 1 | 85.15 | -13 | 106 | 0.862 | |
| Piperidine | 4-Phenylpiperidine | 11 | 15 | 1 | 161.24 | 61 | 257 | 0.998 | |
| Piperidine | 1-Phenylpiperidine | 11 | 15 | 1 | 161.24 | 5 | 260 | 0.996 | |
| Quinoline | Quinoline | 1-Azanapthalene | 9 | 7 | 1 | 129.16 | -15 | 237 | 1.096 |
| Quinoline | Isoquinoline | 9 | 7 | 1 | 129.16 | 27 | 242 | 1.101 | |
| Quinoline | 5,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinoline | 9 | 11 | 1 | 133.19 | 225* | 1.032 | ||
| Quinoline | 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline | 9 | 11 | 1 | 133.19 | -30 | 233 | 1.066 | |
| Quinoline | 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline | 9 | 11 | 1 | 133.19 | 10 | 249 | 1.063 | |
| Quinoline | Perhydroisoquinoline | Decahydroisoquinoline | 9 | 17 | 1 | 139.24 | 212 | 0.938 | |
| Quinoline | Benzo(h)quinoline | 13 | 9 | 1 | 179.22 | 51 | 341 | 1.234 | |
| Quinoline | Acridine | Dibenzo(b,e)pyridine | 13 | 9 | 1 | 179.22 | 111 | 347 | 1.005 |
| Quinoline | Benzo(c)quinoline | Phenanthridine | 13 | 9 | 1 | 179.22 | 107 | 350 | |
| Quinoline | Benzo(f)quinoline | 13 | 9 | 1 | 179.22 | 92 | 352 | ||
| Diamine | N-Methylethylenediamine | 2-(Methylamino)ethylamine | 3 | 10 | 2 | 74.12 | 115 | 0.850 | |
| Diamine | Ethylenediamine | 1,2-Diaminoethane | 2 | 4 | 2 | 56.07 | 9 | 118 | 0.902 |
| Diamine | N-Isopropylethylenediamine | 2-(Isopropylamino)ethylamine | 5 | 14 | 2 | 102.18 | 136 | 0.822 | |
| Diamine | N,N-Diethylethylenediamine | 2-Diethylaminoethylamine | 6 | 16 | 2 | 116.20 | 146 | 0.830 | |
| Diamine | 1,5-Diamino-2-methylpentane | 2-Methyl-1,5-pentanediamine | 6 | 16 | 2 | 116.20 | 193 | 0.863 | |
| Diamine | 1,2-diaminobenzene | o-phenylenediamine | 6 | 8 | 2 | 108.14 | 102 | 256 | |
| Diamine | N-Phenylethylenediamine | 8 | 12 | 2 | 136.19 | 263 | 1.043 | ||
| Diamine | 1,4-diaminobenzene | p-Phenylenediamine | 6 | 8 | 2 | 108.14 | 140 | 267 | |
| Diamine | N-(Phenylmethyl)-1,2-ethane-diamine | 9 | 14 | 2 | 150.22 | 270* | |||
| Diamine | 1,3-diaminobenzene | m-phenylenediamine | 6 | 8 | 2 | 108.14 | 65 | 282 | |
| Diamine | 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine | Hydrazobenzene | 12 | 12 | 2 | 184.24 | 129 | 1.156 | |
| Diamine | 1,1-Diphenylhydrazine | 12 | 12 | 2 | 184.24 | 51 | 344* | 1.188 | |
| Diamine | 1,1-biphenyl-2,2-diamine | 12 | 12 | 2 | 184.24 | 81 | 363* | 1.309 | |
| Diamine | p-Benzidine | 1,1-biphenyl-4,4-diamine | 12 | 12 | 2 | 184.24 | 127 | 401 | |
| Diamine | N,N′-Diphenylethylenediamine | 1,2-Dianilinoethane, | 14 | 16 | 2 | 212.29 | 74 | 404* | |
| * Values estimated for 1 atm from low pressure measurements | |||||||||
Definition of organic compounds
Hydrocarbon: An organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon.
Alkane: An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula CnH2n+2. Also called paraffin.
Aromatic hydrocarbon: A cyclic (ring-shaped), planar (flat) molecule with a ring of resonance bonds that exhibits more stability than other geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms. The simplest of the aromatics have 6 carbon atoms and contains 3 double bounds. A one ring aromatic without any substituents is called benzene, with the formula C6H6.
Alkyl: An alkyl group is an alkane substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula CnH2n+1
Phenyl: An phenyl group is a benzene substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula C6H5.
Organic nitrogen compounds:
Amine: A compound or functional group that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. It can be a primary (R-NH2), a secondary (R',R''-NH) or a tertiary amine (R',R'',R'''-N), where R represent an alkyl or other organic substituent. For 1-amines in this document the R represents an alkyl group, in which the NH2-group is placed at the end of the the alkane chain.
Diamine: An amine with two amino groups.
Pyrrole: A heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with two double bounds, with the formula C4H4NH. Substituted derivatives are called pyrroles.
Dihydropyrrole: A compound formally derived from the aromate pyrrole by partial hydrogenation, containing one double bound. Also called pyrroline.
Pyridine: A heterocyclic six-membered ring compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally similar to benzene, with one methine group (=CH-) replaced by a nitrogen atom.
Piperidine: A heterocyclic amine consisting of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). The molecular formula is (CH2)5NH.
Quinoline: A heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, consisting of a benzene ring fused to a pyridine ring, with the molecular formula C9H7N and the nitrogen atom in position 1.
Isoquinoline: An analog to quinoline with the nitrogen atom in position 2.



