Car Acceleration
Car acceleration calculator.
If you know the initial and final velocity of a car (or whatever) - and the time used - the average acceleration can be calculated as
a = dv / dt
= (vf - vs ) / dt (1)
where
a = acceleration of object (m/s2, ft/s2)
dv = change in velocity (m/s, ft/s)
vf = final speed (m/s, ft/s)
vs = start speed (m/s, ft/s)
dt = time used (s)
Common benchmark velocities for acceleration of cars and motorcycles are
- 0 - 60 mph = 0 - 26.8 m/s = 0 - 96.6 km/h
- 0 - 100 km/h = 0 - 27.8 m/s = 0 - 62.1 mph
Online Car Acceleration Calculator
km/h
Note that force, work and power are calculated for mass acceleration only. Forces due to air resistance ( drag) and rolling friction are not included.
mph
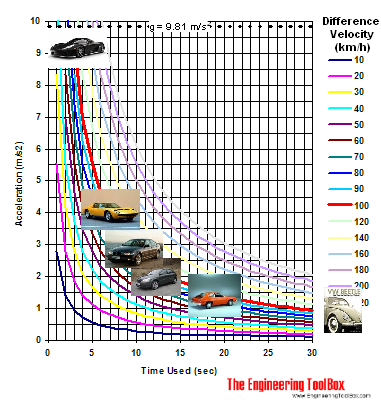
Car Acceleration Diagram - km/h

Download and Print Car Acceleration Chart
Car Acceleration Diagram - mph
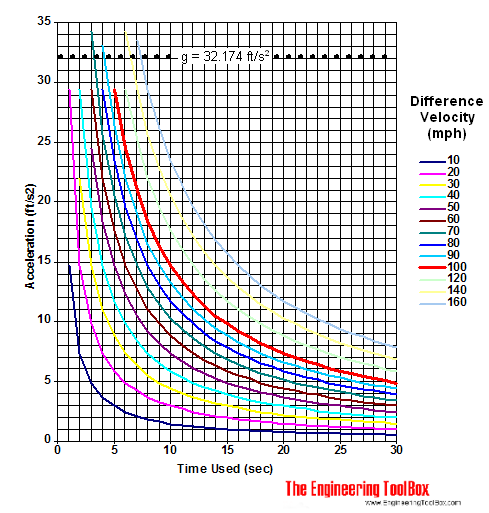
Download and Print Car Acceleration Chart
If you know the distance moved and the time used - the acceleration can be calculated as
a = 2 ds / dt2 (2)
where
ds = distance moved (m, ft)
Acceleration of some known cars
Acceleration Force
The acceleration force can be calculated as
F = m a (3)
where
F = acceleration force (N, lbf)
m = mass of car (kg, slugs)
Acceleration Work
The acceleration work can be calculated as
W = F l (4)
where
W = work done (Nm, J, ft lbf)
l = distance moved (m, ft)
Acceleration Power
The acceleration power can be calculated as
P = W / dt (5)
where
P = power (J/s, W, ft lbf/s)
Example - Car Acceleration
A car with mass 1000 kg (2205 lbm) accelerates from 0 m/s (0 ft/s) to 27.8 m/s (100 km/h, 91.1 ft/s, 62.1 mph) in 10 s .
The average acceleration can be calculated from eq. 1 as
a = ((27.8 m/s) - (0 m/s)) / (10 s)
= 2.78 m/s2
The average acceleration force can be calculated from eq. 3 as
F = (1000 kg) (2.78 m/s2)
= 2780 N
The distance moved can be calculated by rearranging eq. 2 to
ds = a dt2/ 2
= (2.78 m/s2) (10 s)2/ 2
= 139 m
The average acceleration work can be calculated from eq. 4 as
W = (2780 N) (139 m)
= 386420 J
The average acceleration power can be calculated from eq. 5 as
P = (386420 J) / (10 s)
= 38642 W
= 38.6 kW
The calculation can also be done in Imperial units :
The average acceleration can be calculated from eq. 1 as
a = ((91.1 ft/s) - (0 ft/s)) / (10 s)
= 9.11 ft/s2
In the Imperial system mass is measured in slugs where 1 slug = 32.17405 lbm
The average acceleration force can be calculated from eq. 3 as
F = (( 2205 lbm) (1/32.17405 (slugs/ lbm))) (9.11 ft/s2)
= 624 lbf
The distance moved can be calculated by rearranging eq. 2 to
ds = a dt2/ 2
= (9.11 ft/s2) (10 s)2/ 2
= 455 ft
The average acceleration work can be calculated from eq. 4 as
W = (624 lbf) (455 ft)
= 284075 ft lbf
- 1 ft lbf = 1.36 J
The average acceleration power can be calculated from eq. 5 as
P = (284075 ft lbf) / (10 s)
= 28407 ft lbf/s
- 1 ft lbf/s = 1.36 W = 0.00182 hp
Note that acceleration of a car varies due to gear shifts and motor characteristics.



