Centripetal and Centrifugal Acceleration Force
Forces due to circular motion and centripetal / centrifugal acceleration.
Centripetal and Centrifugal Force are the action-reaction force pair associated with circular motion.
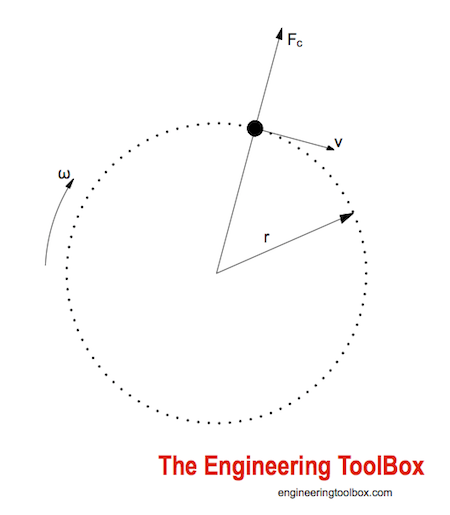
Centripetal Acceleration
Velocity is a vector - specifying how fast (or slow) a distance is covered and the direction of the movement. Since the velocity vector (the direction) of a body changes when moved in a circle - there is an acceleration.
This acceleration is named the centripetal acceleration - and can be expressed as
ac = v2 / r
= ω2 r
= (2 π nrps )2 r
= (2 π nrpm / 60)2 r
(π nrpm / 30)2 r (1)
where
ac = centripetal acceleration (m/s2, ft/s2)
v = tangential velocity (m/s, ft/s)
r = circular radius (m, ft)
ω = angular velocity ( rad /s)
nrps = revolutions per second (rev/s, 1/s)
nrpm = revolutions per min (rev/min, 1/min)
Centripetal Force
According Newton's second law the centripetal force can be expressed as
Fc = m ac
= m v2 / r
= m ω2 r
= m (2 π ns )2 r
= m (2 π nrpm / 60)2 r
= m (π nrpm / 30)2 r (2)
where
Fc = centripetal force (N, lbf)
m = mass (kg, slugs)
According to Newton's Third Law the centripetal force acting on the object has a centrifugal force of the same magnitude acting in the opposite direction.
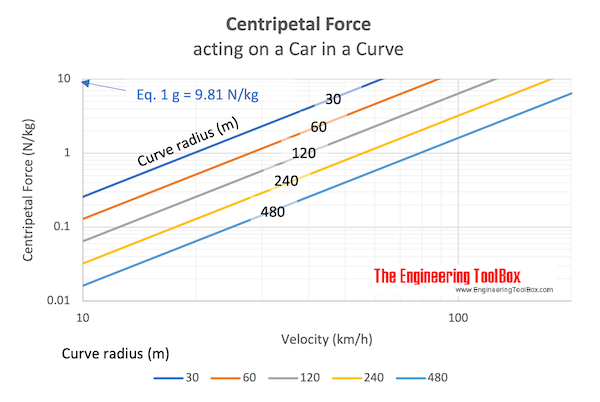
Example - the Centripetal Acceleration and Force acting on a Car through a Curve

Metric Units
A car with mass 1000 kg drives through a curve with radius 200 m at speed 50 km/h. The centripetal acceleration can be calculated as
ac = ((50 km/h) (1000 m/km) (1/3600 h/s))2 / (200 m)
= 0.965 m/s2
= 0.1 g
where
1 g = acceleration of gravity (9.81 m/s2)
The centripetal force can bee calculated as
Fc = (1000 kg) ( 0.965 m/s2)
= 965 N
= 0.97 kN
Related to the gravity force - weight :
Fg = (1000 kg) (9.81 m/s2)
= 9810 N
= 9.8 kN
Imperial Units
A car with weight (gravity force) 3000 lb travels through a curve with radius 100 ft with speed 15 miles/h .
The mass of the car can be calculated as
m = (3000 lb) / (32 ft/s2)
= 94 slugs
The centripetal acceleration can be calculated as
ac = ((15 miles/h)(5280 ft/mile) / (3600 s/h))2/ (100 ft)
= 4.84 ft/s2
The centripetal force can bee calculated as
Fc = (94 slugs) (4.84 ft/s2)
= 455 lbf
Centripetal (Centrifugal) Calculator - velocity
This calculator can be used if the velocity of an object is known - like a car in a turning curve.
Centripetal (Centrifugal) Force - rpm
Equation (2) can be modified to express centripetal or centrifugal force as a function of revolution per minute - rpm - as
Fc = 0.01097 m r nrpm2 (3)
where
nrpm = revolution per minute (rpm)
Centripetal (Centrifugal) Calculator - rpm
This calculator can be used if revolution speed of an object is known - like a turning bowl in a lathe.
Centrifugal Force
Force is an abstraction representing the push and pull interaction between objects. Newton's third law states that
- for every acting force there is an equal and opposite reaction force
Therefore there must be an equal and opposite reaction force to the Centripetal Force - the Centrifugal Force.