Velocity Pressure Head
Dynamic pressure or velocity head.
The dynamic pressure in a fluid flow can be expressed as
pd = 1/2 ρf v 2 (1)
where
pd = dynamic pressure in fluid (Pa, psf (lb/ft2))
ρf = density of fluid (kg/m3, slugs /ft3)
v = fluid velocity (m/s, ft/s)
- 1 Pa = 10-6 N/mm2 = 10-5 bar = 0.1020 kp/m2 = 1.02×10-4 m H2O = 9.869×10-6 atm = 1.45×10-4 psi (lbf/in2)
- 1 psf (lbf/ft2) = 47.88 N/m2(Pa) = 0.006944 lbf/in2(psi)
Head loss as water column can be calculated by dividing the dynamic pressure with the specific weight of water like
hw = pd / γw
= (1/2 ρf v2) / (ρw g)
= ρf v2 / (2 ρw g) (2)
where
hw = head water (m Water, ft Water)
γw = ρw g = specific weight water (9807 N/m3, 62.4 l bf/ft3)
where
ρw = density of water (1000 kg/m3, 1.940 slugs/ft3)
g = acceleration of gravity ( 9.81 m/s2, 32.174 ft/s2)
Water Flow
If the flowing fluid is water - then ρf = ρw , and (2) can be modified to
hw = v2 / 2 g (3)
Or simplified to
Metric Units
hw(m H2O) = 0.051 v2 (3b)
hw(mm H2O) = 51 v2 (3c)
where
v = velocity (m/s)
Imperial Units
hw(ft H2O) = 0.0155 vfps 2 (3d)
hw(in H2O) = 0.186 vfps 2 (3e)
where
vfps = velocity (ft/s)
or
hw(ft H2O) = 0.0155 (vfpm / 60)2 (3f)
hw(in H2O) = 0.186 (vfpm / 60)2 (3g)
where
vfpm = velocity (ft/min)
Water Flow - Head to Velocity Calculator
This calculator can be used to calculate water velocity in a pipe or water stream from a measured head of water column. The dynamic pressure as head is typically measured with a pitot tube.
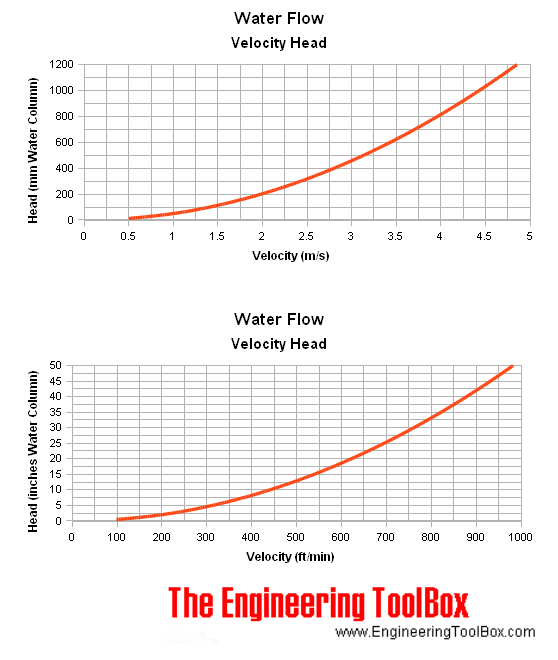
Water Flow - Velocity and Dynamic Head Chart
Water Flow - Velocity Heads
| Water Flow Velocity - v - (ft/sec) | Velocity Head - hw - (ft H2O) |
|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.004 |
| 1.0 | 0.016 |
| 1.5 | 0.035 |
| 2.0 | 0.062 |
| 2.5 | 0.097 |
| 3.0 | 0.140 |
| 3.5 | 0.190 |
| 4.0 | 0.248 |
| 4.5 | 0.314 |
| 5.0 | 0.389 |
| 5.5 | 0.470 |
| 6.0 | 0.560 |
| 6.5 | 0.657 |
| 7.0 | 0.762 |
| 7.5 | 0.875 |
| 8.0 | 0.995 |
| 8.5 | 1.123 |
| 9.0 | 1.259 |
| 9.5 | 1.403 |
| 10.0 | 1.555 |
| 11.0 | 1.881 |
| 12.0 | 2.239 |
| 13.0 | 2.627 |
| 14.0 | 3.047 |
| 15.0 | 3.498 |
| 16.0 | 3.980 |
| 17.0 | 4.493 |
| 18.0 | 5.037 |
| 19.0 | 5.613 |
| 20.0 | 6.219 |
| 21.0 | 6.856 |
| 22.0 | 7.525 |
- 1 ft (foot) = 0.3048 m = 12 inches = 0.3333 yd
Air Flow
Metric Units
If the flowing fluid is air with ρf = 1.205 kg/m3 (20 oC) and the reference fluid is water with ρw = 1000 kg/m3 - (2) can be simplified to
hw(m H2O) = ((1.205 kg/m3) v2) / (2 (1000 kg/m3) 9.81 m/s2)
= 6.1×10-5 v2 (4)
where
v = air velocity (m/s)
or
hw(mm H2O) = 6.1×10-2 v2 (4b)
Note! - these simplified equations must be relaculated for other air temperatures and densities.
Imperial Units
hw(ftH2O) = (v / C)2 / 12 (4c)
hw(inH2O) = (v / C)2 (4d)
where
v = velocity (ft/min)
C = constant (4005 for temperature 70 oF)
The constant C and temperature:
| Air Temperature (oF) | C |
|---|---|
| 35 | 3872 |
| 40 | 3891 |
| 45 | 3910 |
| 50 | 3932 |
| 55 | 3952 |
| 60 | 3970 |
| 65 | 3987 |
| 70 | 4005 |
| 75 | 4025 |
| 80 | 4045 |
| 85 | 4064 |
| 90 | 4081 |
| 95 | 4101 |
| 100 | 4117 |
| 150 | 4298 |
Air Flow - Head to Velocity Calculator
This calculator can be used to calculate air velocity in a duct or air stream from a measured head of water column. The dynamic pressure as head is typically measured with a pitot tube.
Velocity and Dynamic Head Chart
Charts are based on air density 1.205 kg/m3 and water density 1000 kg/m3.
Air Flow - Velocity Heads
Table based on ρf = 1.205 kg/m3 (C = 4005, temperature 70 oF) and ρw = 1000 kg/m3 (1.940 slugs/ft3) .
| Air Flow Velocity - v - (ft/sec) | Velocity Head - hw - (ft H2O) |
|---|---|
| 5 | 0.00047 |
| 10 | 0.0019 |
| 15 | 0.0042 |
| 20 | 0.0075 |
| 25 | 0.012 |
| 30 | 0.017 |
| 35 | 0.023 |
| 40 | 0.030 |
| 45 | 0.038 |
| 50 | 0.047 |
| 55 | 0.057 |
| 60 | 0.067 |
| 65 | 0.079 |
| 70 | 0.092 |
| 75 | 0.11 |
| 80 | 0.12 |
| 85 | 0.14 |
| 90 | 0.15 |
| 95 | 0.17 |
| 100 | 0.19 |