Pump Power Calculator: Calculate Hydraulic and Shaft Power for Pumps
Calculate pumps hydraulic and shaft power.
Hydraulic Pump Power
The ideal hydraulic power to drive a pump depends on
- the mass flow rate the
- liquid density
- the differential height
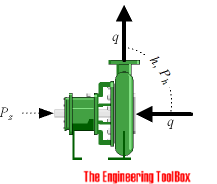
- either it is the static lift from one height to an other or the total head loss component of the system - and can be calculated like
Ph(kW) = q ρ g h / 3.6×106
= q p / 3.6×106 (1)
where
Ph(kW) = hydraulic power (kW)
q = flow (m3/h)
ρ = density of fluid (kg/m3)
g = acceleration of gravity (9.81 m/s2)
h = differential head (m)
p = differential pressure (N/m2, Pa)
The hydraulic Horse Power can be calculated as:
Ph(hp) = Ph(kW) / 0.746 (2)
where
Ph(hp) = hydraulic horsepower (hp)
Or - alternatively
Ph(hp) = qgpm hft SG / (3960 η) (2b)
where
qgpm = flow (gpm)
hft = differential head (ft)
SG = Specific Gravity (1 for water)
η = pump efficiency (0..1)
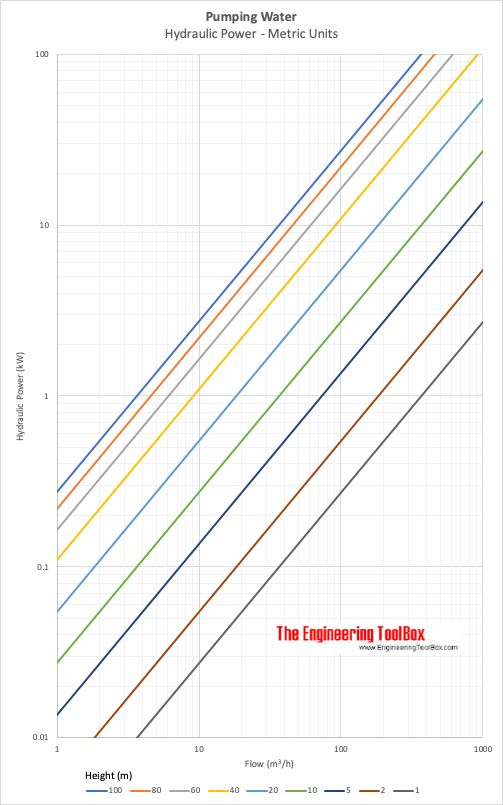
Example - Power pumping Water, SI Units
1 m3/h of water is pumped a head of 10 m. The theoretical pump power can be calculated as
Ph(kW) = (1 m3/h) (1000 kg/m3) (9.81 m/s2) (10 m) / (3.6×106)
= 0.027 kW
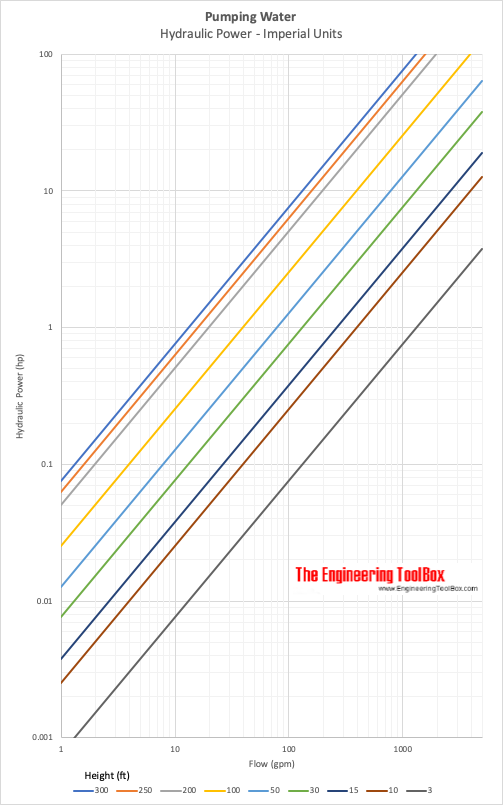
Example - Power pumping Water, Imperial Units
600 gpm of water is pumped a head of 110 ft. The efficiency ofthe pump i s 60% (0.6) and the specific gravity of water is 1. The pump shaft power can be calculated as
Ph(kW) = (600 gpm) (110 ft) (1) / ((3960) (0.6))
= 27.8 hp
Shaft Pump Power
The shaft power - the power required transferred from the motor to the shaft of the pump - depends on the efficiency of the pump and can be calculated as
Ps(kW) = Ph(kW) / η (3)
where
Ps(kW) = shaft power (kW)
η = pump efficiency (0..1)
Online Pump Calculator - SI-units
The calculator below can used to calculate the hydraulic and shaft power of a pump:
Online Pump Calculator - Imperial units
The calculator below can used to calculate the hydraulic and shaft power of a pump using Imperial units:
- Specific weight of water is 62.4 lb/ft3
- Check the relation between Density, Specific Weight and Specific Gravity
- Make Shortcut to this Calculator on Your Home Screen?
Related Mobile Apps from The Engineering ToolBox
- free apps for offline use on mobile devices.