Insulation Materials - Operating Temperature Limits
Temperature limits for commonly used insulation materials.
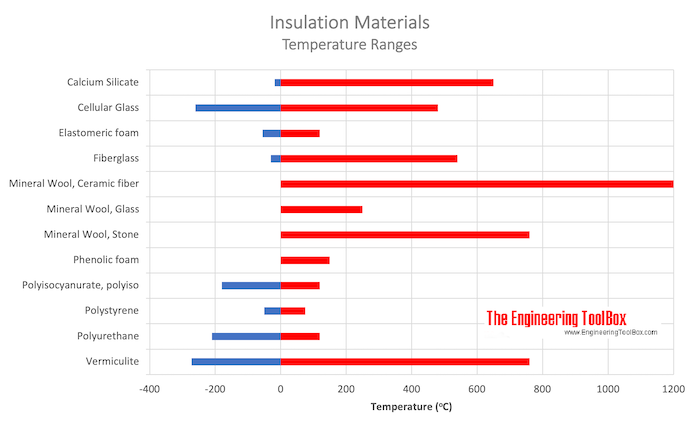
Temperature limits for some commonly used insulation materials:
| Insulation Material | Temperature Range | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | |||
| (oC) | (oF) | (oC) | (oF) | |
| Calcium Silicate | -18 | 0 | 650 | 1200 |
| Cellular Glass | -260 | -450 | 480 | 900 |
| Elastomeric foam | -55 | -70 | 120 | 250 |
| Fiberglass | -30 | -20 | 540 | 1000 |
| Mineral Wool, Ceramic fiber | 1200 | 2200 | ||
| Mineral Wool, Glass | 0 | 32 | 250 | 480 |
| Mineral Wool, Stone | 0 | 32 | 760 | 1400 |
| Phenolic foam | 150 | 300 | ||
| Polyisocyanurate, polyiso | -180 | -290 | 120 | 250 |
| Polystyrene | -50 | -60 | 75 | 165 |
| Polyurethane | -210 | -350 | 120 | 250 |
| Vermiculite | -272 | -459 | 760 | 1400 |
Calcium Silicate Insulation
Non-asbestos Calcium Silicate insulation board and pipe insulation feature with light weight, low thermal conductivity, high temperature and chemical resistance.
Cellular Glass Insulation
Cellular glass insulation is composed of crushed glass combined with a cellulating agent.
These components are mixed, placed in a mold, and then heated to a temperature of approximately 950 oF. During the heating process, the crushed glass turns to a liquid. Decomposition of the cellulating agent will cause the mixture to expand and fill the mold. The mixture creates millions of connected, uniform, closed-cells and form at the end a rigid insulating material.
Cellulose Insulation
Cellulose is made from shredded recycled paper, such as newsprint or cardboard. It's treated with chemicals to make it fire- and insect-resistant, and is applied as loose-fill or wet-sprayed through a machine.
Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass is the most common type of insulation. It's made from molten glass spun into microfibers.
Mineral Wool Insulation

Mineral wool is made from molten glass, stone, ceramic fibre or slag that is spun into a fiber-like structure. Inorganic rock or slag are the main components (typically 98%) of stone wool. The remaining 2% organic content is generally a thermosetting resin binder (an adhesive) and a little oil.
Polyurethane insulation
Polyurethane is an organic polymer formed by reacting a polyol (an alcohol with more than two reactive hydroxyl groups per molecule) with a diisocyanate or a polymeric isocyanate in the presence of suitable catalysts and additives.
Polyurethanes are flexible foams used in mattresses, chemical-resistant coatings, adhesives and sealants, insulation for buildings and technical applications like heat exchangers, cooling pipes and much more.
Polystyrene Insulation
Polystyrene is an excellent insulator. It is manufactured in two ways:
- Extrusion - which results in fine, closed cells, containing a mixture of air and refrigerant gas
- Molded or expanded - which produces coarse, closed cells containing air
Extruded polystyrene, or XPS, is a closed-cell, thermal plastic material manufactured by a variety of extrusion processes. The main applications of extruded polystyrene insulation are in building insulation and construction in general.
Molded or expanded polystyrene is commonly called beadboard and has a lower R-value than extruded polystyrene.
Polyisocyanurate (polyiso) Insulation
Polyisocyanurate or polyiso is a thermosetting type of plastic, a closed-cell foam that contains a low-conductivity gas in its cells.