Ammonia - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables showing dynamic (absolute) and kinematic viscosity of gasous and liquid ammonia at temperatures ranging from -73 to 425°C (-100 to 800°F) at pressure ranging from 1 to 1000 bara (14.5 - 14500 psia) - SI and Imperial Units.
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress .
For further definitions, go to Absolute (dynamic) and kinematic viscosity . Absolute or dynamic viscosity is used to calculate Reynold's Number to determine if a fluid flow is laminar, transient or turbulent.
Tabulated values and viscosity units conversion are given below the figures.
Online Ammonia Gas Viscosity Calculator
The calculator below can be used to calculate dynamic or kinematic viscosity of gaseous ammonia at given temperatures and atmospheric pressure.
The output dynamic viscosity is given as Pas, Ns/m2, cP, mPas, lbfs/ft2 and lbm/fth, while the kinematic viscosity is given as cSt, m2/s and ft2/s.
Note! Temperature must be within the ranges -33 - 427 °C, -28 - 800 °F, 240 - 700 K and 432-1260 °R to get valid values.
See also other properties of Ammonia at varying temperature and pressure: Density and specific weight, Dynamic and kinematic viscosity, Prandtl Number, Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium pressure, Specific Heat (Heat Capacity) and Thermal Conductivity, and Thermophysical properties at standard conditions and Vapour pressure at gas-liquid equilibrium,
as well as dynamic and kinematic viscosity of air, benzene, butane, carbon dioxide, ethane, ethanol, ethylene, methane, methanol, nitrogen, oxygen, propane and water.
Gaseous ammonia dynamic and kinematic viscosity at atmospheric pressure and varying temperature:
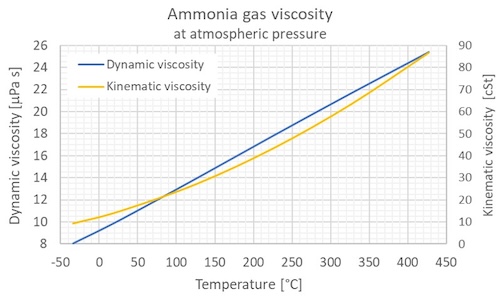
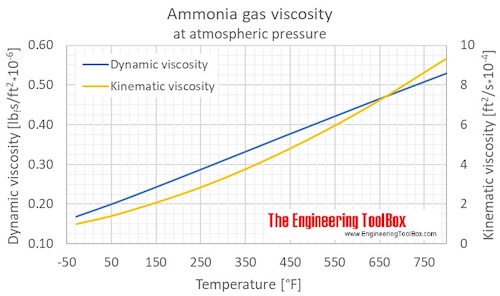
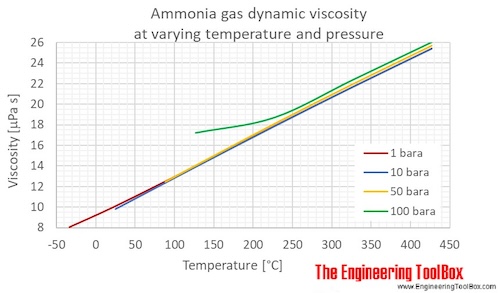
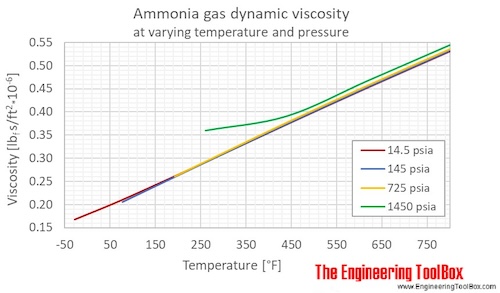
Gaseous ammonia dynamic viscosity at varying temperature and constant pressures (1-1000 bara, 14.5 - 14500 psia):
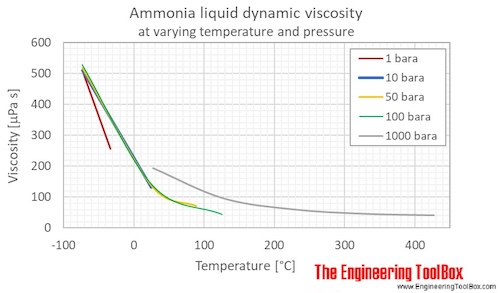
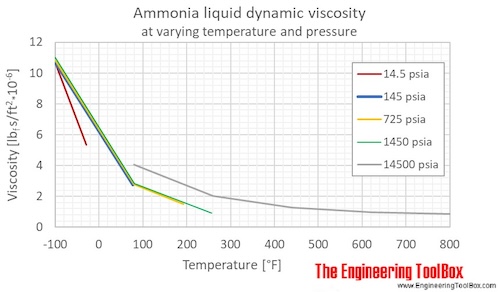
Liquid ammonia dynamic viscosity at varying temperature and constant pressures (1-1000 bara, 14.5 - 14500 psia):
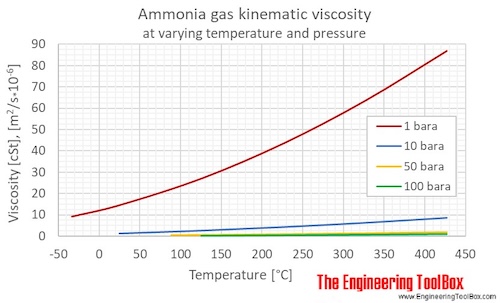
Gaseous ammonia kinematic viscosity at varying temperature and constant pressures (1-10 000 bara, 14.5 - 145 000 psia):
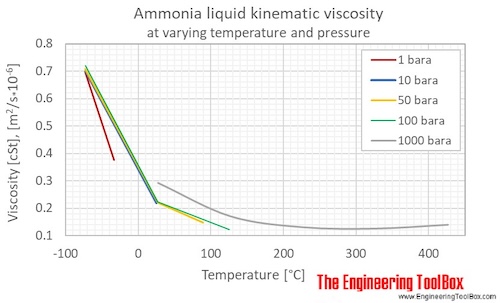
Ammonia dynamic and kinematic viscosity at gas-liquid equilibrium pressure: 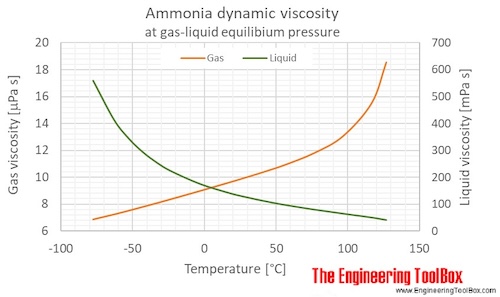
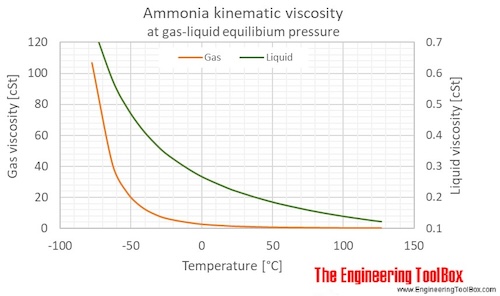
Dynamic (absolute) and kinematic viscosity of ammonia at given temperatures and pressures:
For full table with Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity - rotate the screen!
| State | Temperature | Pressure | Dynamic (absolute) viscosity | Kinematic vicosity | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (K) | (°C) | (°F) | (MPa) | (bara) | (psia) | (μPa s) | (cP) | (lbf s/ft2 ×10-6) | (lbm/ft s ×10-6) | (lbm/ft h) | (cSt), (m2/s ×10-6) | (ft2/s ×10-6) | |
| Liquid | 200 | -73.2 | -99.7 | 0.1 | 1 | 15 | 507.7 | 0.5077 | 10.60 | 341.2 | 1.228 | 0.6972 | 7.505 |
| 239.6 | -33.6 | -28.5 | 0.1 | 1 | 15 | 256.4 | 0.2564 | 5.355 | 172.3 | 0.6203 | 0.3758 | 4.045 | |
| Gas | 239.6 | -33.6 | -28.5 | 0.1 | 1 | 15 | 8.05 | 0.008046 | 0.1680 | 5.407 | 0.01946 | 9.156 | 98.56 |
| 300 | 26.9 | 80.3 | 0.1 | 1 | 15 | 10.16 | 0.010161 | 0.2122 | 6.828 | 0.02458 | 14.73 | 158.6 | |
| 400 | 127 | 260 | 0.1 | 1 | 15 | 13.97 | 0.013971 | 0.2918 | 9.388 | 0.03380 | 27.19 | 292.7 | |
| 500 | 227 | 440 | 0.1 | 1 | 15 | 17.86 | 0.017863 | 0.3731 | 12.00 | 0.04321 | 43.54 | 468.6 | |
| 600 | 327 | 620 | 0.1 | 1 | 15 | 21.68 | 0.021682 | 0.4528 | 14.57 | 0.05245 | 63.46 | 683.1 | |
| 700 | 427 | 800 | 0.1 | 1 | 15 | 25.39 | 0.025391 | 0.5303 | 17.06 | 0.06142 | 86.74 | 933.6 | |
| Liquid | 200 | -73.2 | -99.7 | 1 | 10 | 145 | 509.3 | 0.5093 | 10.64 | 342.2 | 1.232 | 0.6991 | 7.525 |
| 298.1 | 24.9 | 76.8 | 1 | 10 | 145 | 131.8 | 0.1318 | 2.753 | 88.58 | 0.3189 | 0.2186 | 2.353 | |
| Gas | 298.1 | 24.9 | 76.8 | 1 | 10 | 145 | 9.831 | 0.009831 | 0.2053 | 6.606 | 0.02378 | 1.256 | 13.52 |
| 300 | 26.9 | 80.3 | 1 | 10 | 145 | 9.912 | 0.009912 | 0.2070 | 6.660 | 0.02398 | 1.287 | 13.85 | |
| 400 | 127 | 260 | 1 | 10 | 145 | 13.93 | 0.01393 | 0.2909 | 9.359 | 0.03369 | 2.625 | 28.25 | |
| 500 | 227 | 440 | 1 | 10 | 145 | 17.88 | 0.01788 | 0.3734 | 12.01 | 0.04325 | 4.297 | 46.26 | |
| 600 | 327 | 620 | 1 | 10 | 145 | 21.72 | 0.02172 | 0.4536 | 14.59 | 0.05254 | 6.314 | 67.96 | |
| 700 | 427 | 800 | 1 | 10 | 145 | 25.43 | 0.02543 | 0.5312 | 17.09 | 0.06153 | 8.642 | 93.03 | |
| Liquid | 200 | -73.2 | -99.7 | 5 | 50 | 725 | 517.3 | 0.5173 | 10.80 | 347.6 | 1.251 | 0.7088 | 7.630 |
| 300 | 26.9 | 80.3 | 5 | 50 | 725 | 132.5 | 0.1325 | 2.767 | 89.03 | 0.3205 | 0.2194 | 2.362 | |
| 362.0 | 88.9 | 192.0 | 5 | 50 | 725 | 71.29 | 0.0713 | 1.489 | 47.91 | 0.1725 | 0.1468 | 1.581 | |
| Gas | 362.0 | 88.9 | 192 | 5 | 50 | 725 | 12.48 | 0.01248 | 0.2605 | 8.383 | 0.03018 | 0.2950 | 3.176 |
| 400 | 127 | 260 | 5 | 50 | 725 | 14.04 | 0.01404 | 0.2931 | 9.432 | 0.03395 | 0.4406 | 4.742 | |
| 500 | 227 | 440 | 5 | 50 | 725 | 18.07 | 0.01807 | 0.3775 | 12.14 | 0.04372 | 0.8134 | 8.756 | |
| 600 | 327 | 620 | 5 | 50 | 725 | 21.94 | 0.02194 | 0.4582 | 14.74 | 0.05308 | 1.237 | 13.31 | |
| 700 | 427 | 800 | 5 | 50 | 725 | 25.66 | 0.02566 | 0.5360 | 17.24 | 0.06208 | 1.721 | 18.52 | |
| Liquid | 200 | -73.2 | -99.7 | 10 | 100 | 1450 | 527.3 | 0.5273 | 11.013 | 354.3 | 1.276 | 0.7209 | 7.760 |
| 300 | 26.9 | 80.3 | 10 | 100 | 1450 | 136.4 | 0.1364 | 2.848 | 91.63 | 0.3299 | 0.2242 | 2.413 | |
| 398.3 | 125 | 257 | 10 | 100 | 1450 | 43.63 | 0.043632 | 0.9113 | 29.32 | 0.1055 | 0.1223 | 1.317 | |
| Gas | 398.3 | 125 | 257 | 10 | 100 | 1450 | 17.79 | 0.01779 | 0.3716 | 11.96 | 0.04304 | 0.1463 | 1.575 |
| 400 | 127 | 260 | 10 | 100 | 1450 | 17.23 | 0.01723 | 0.3599 | 11.58 | 0.04168 | 0.1546 | 1.664 | |
| 500 | 227 | 440 | 10 | 100 | 1450 | 18.72 | 0.01872 | 0.3910 | 12.58 | 0.04529 | 0.3836 | 4.129 | |
| 600 | 327 | 620 | 10 | 100 | 1450 | 22.39 | 0.02239 | 0.4677 | 15.05 | 0.05417 | 0.6073 | 6.537 | |
| 700 | 427 | 800 | 10 | 100 | 1450 | 26.04 | 0.02604 | 0.5438 | 17.49 | 0.06298 | 0.8571 | 9.226 | |
| Liquid | 300 | 26.9 | 80.3 | 100 | 1000 | 14500 | 193.7 | 0.1937 | 4.046 | 130.2 | 0.4686 | 0.2917 | 3.140 |
| 400 | 127 | 260 | 100 | 1000 | 14500 | 96.24 | 0.09624 | 2.010 | 64.67 | 0.2328 | 0.1707 | 1.837 | |
| 500 | 227 | 440 | 100 | 1000 | 14500 | 60.39 | 0.06039 | 1.261 | 40.58 | 0.1461 | 0.1310 | 1.410 | |
| 600 | 327 | 620 | 100 | 1000 | 14500 | 46.19 | 0.04619 | 0.9647 | 31.04 | 0.1117 | 0.1260 | 1.357 | |
| 700 | 427 | 800 | 100 | 1000 | 14500 | 41.24 | 0.04124 | 0.8613 | 27.71 | 0.0998 | 0.1399 | 1.506 | |
Viscosity Dynamic, Absolute
centipoise (cP), gram/(centimeter second) (g/(cm s)) = poise (P), kilogram/meter second (kg/m s)=newton second/square meter (N s/m2)= pascal second (Pa s), pound/(foot hour) (lb/(ft h)), pound/(foot second) (lb/(ft s)), reyn (reyn)
- 1 cP = 0.001 Pa s = 0.01 P = 0.01 g/(cm sec) = 6.72197×10-4 lb/(ft s) = 2.4191 lb/(ft h)
- 1 lb/(ft h) = 0.00027778 lb/(ft s) = 0.00041338 Pa s = 0.0041338 P = 0.41338 cP
- 1 lb/(ft s) = 3600 lb/(ft h) = 1.48816 Pa s = 14.8816 P = 1488.16 cP
- 1 kg/(m s) = 1 (N s)/m2= 1 Pa s = 10 P = 1000 cP = 0.672197 lb/(ft s) = 2419.09 lb/(ft h)
- 1 (N s)/m2= 1 kg/(m s) = 1 Pa s = 10 P = 1000 cP = 0.672197 lb/(ft s) = 2419.09 lb/(ft h)
- 1 P = 1 g/(cm s) = 0.1 Pa s = 100 cP = 0.067197 lb/(ft s) = 241.909 lb/(ft h)
- 1 Pa s = 1 kg/(m s) = 1 (N s)/m2= 10 P = 1000 cP = 0.672197 lb/(ft s) = 2419.08 lb/(ft h) = 0.00014504 reyn
- 1 reyn = 6894.76 Pa s
See also Absolute or Dynamic Viscosity Unit Converter
Viscosity Kinematic
centistoke (cSt) = square millimeter/second (mm2/s), square foot/hour (ft2/h), square foot/second (ft2/s), square inch/second (in2/s), square meter/hour (m2/h), square meter/second (m2/s), stoke (St) = square centimeter/second (cm2/s)
- 1 cm2/s = 1 St = 100 mm2/s = 100 cSt = 1×10-4 m2/s = 0.36 m2/h = 1.07639×10-3 ft2/s = 3.875008 ft2/h = 0.1550003 in2/s
- 1 cSt = 1 mm2/s = 0.01 St = 1×10-6 m2/s = 0.0036 m2/h = 1.07639×10-5ft2/s = 0.03875008 ft2/h = 0.001550003 in2/s
- 1 ft2/h = 2.7778×10-4 ft2/s = 0.04 in2/s = 2.58064×10-5m2/s = 0.09290304 m2/h = 25.8064 cS = 0.258064 St
- 1 ft2/s = 3600 ft2/h = 144 in2/s = 0.09290304 m2/s = 334.451 m2/h = 92903.04 cSt = 929.0304 St
- 1 in2/s = 0.0069444 ft2/s = 25 ft2/h = 0.00064516 m2/s = 2.322576 m2/h = 645.16 cSt = 6.4516 St
- 1 m2/h = 1/3600 m2/s = 2.7778×10-4 m2/s = 2.7778 cm2/s = 277.78 mm2/s = 277.78 cSt = 2.7778 St = 0.00298998 ft2/s = 10.7639 ft2/h = 0.430556 in2/s
- 1 m2/s = 3600 m2/h = 1×104 cm2/s = 1×104 St = 1×106 mm2/s = 1×106 cSt = 10.7639 ft2/s = 38750.08 ft2/h = 1550003 in2/s
- 1 mm2/s = 1 cSt = 1×10-6 m2/s = 0.0036 m2/h = 0.01 cm2/s = 0.01 St = 1.07639×10-5ft2/s = 0.03875008 ft2/h = 0.001550003 in2/s
- 1 St = 1 cm2/s = 100 cSt = 100 mm2/s = 1×10-4 m2/s = 0.36 m2/h = 1.076×10-3 ft2/s = 3.875008 ft2/h = 0.1550003 in2/s
See also Kinematic Viscosity Unit Converter



