Water - Absolute (Dynamic) Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Absolute viscosity for water in centipoises for temperatures between 32 - 200oF.
Absolute or dynamic viscosity is used to calculate Reynolds Number to determine if a fluid flow is laminar, transient or turbulent.
- Reynold's Number - a definition
The absolute or dynamic viscosity of water depends on the temperature as indicated below:
| Temperature | Absolute - Dynamic - Viscosity (cP) | |
|---|---|---|
| (oF) | (oC) | |
| 32 | 0 | 1.794 |
| 40 | 4.4 | 1.546 |
| 50 | 10.0 | 1.310 |
| 60 | 15.6 | 1.129 |
| 70 | 21.1 | 0.982 |
| 80 | 26.7 | 0.862 |
| 90 | 32.2 | 0.764 |
| 100 | 37.8 | 0.682 |
| 120 | 48.9 | 0.559 |
| 140 | 60.0 | 0.470 |
| 160 | 71.1 | 0.401 |
| 180 | 82.2 | 0.347 |
| 200 | 93.3 | 0.305 |
- 1 cP = 0.01 poise = 0.01 gram per cm second = 0.001 Pascal second = 1 milliPascal second = 0.001 N.s/m2
- Convert viscosity
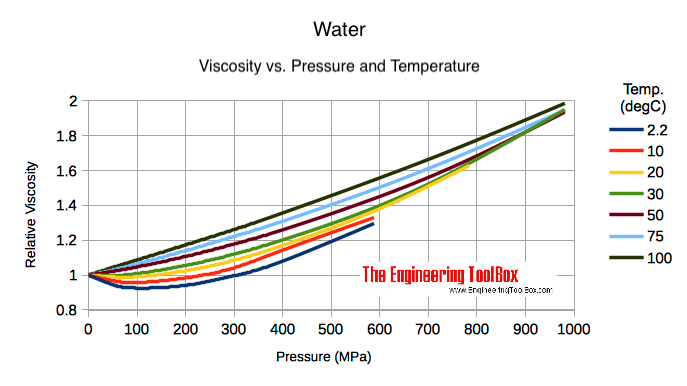
Water - Relative Viscosity vs. Higher Pressure and Temperature