Secondary Coolants - Properties
Comparing properties like specific gravity, freezing points and viscosity for secondary coolants like calcium chloride, sodium chloride, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol.
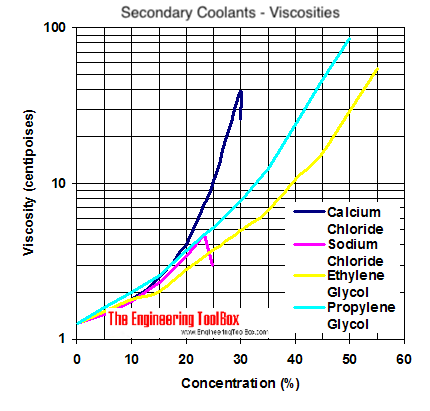
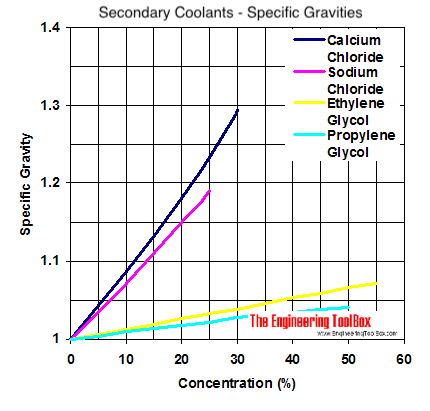
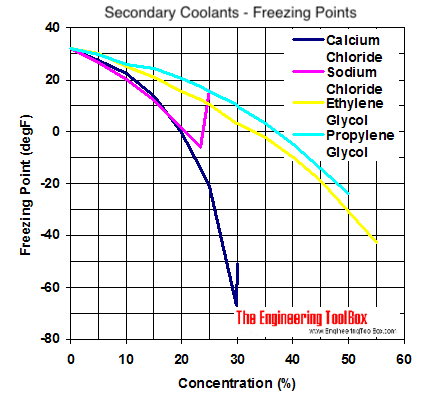
The diagrams below can be used to compare specific gravity, freezing points and viscosity of secondary coolants
- ethylene glycol
- propylene glycol
- calcium chloride
- sodium chloride
Specific Gravities
Freezing Points
- tC = 5/9(tF - 32)
Viscosities