Process Pipes - Allowable Stress vs. Temperature
Allowable wall stress in pipes according ASME M31.3.
Operating temperatures and allowable tension stresses according ASME B31.3 - Process Piping.
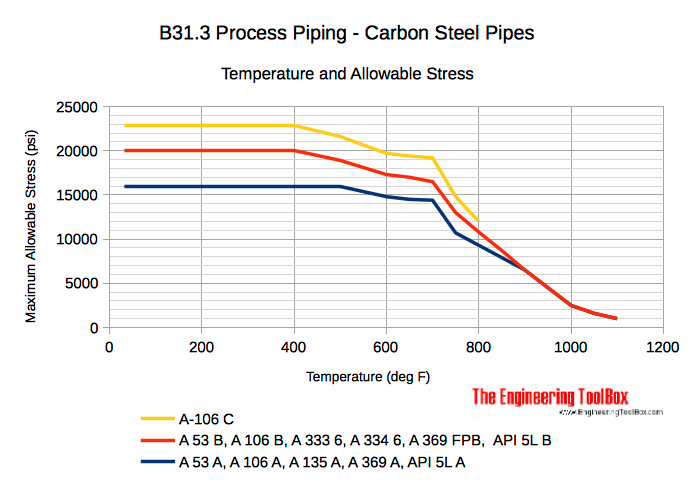
Carbon Steel Pipes and Tubes
- A 53 Pipe, Steel, Black and Hot-Dipped, Zinc Coated, Welded and Seamless
- A 106 Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service
- A 135 Standard Specification for Electric-Resistance-Welded Steel Pipe
- A 333 Seamless and Welded Steel Pipe for Low-Temperature Service
- A 334 Seamless and Welded Carbon and Alloy-Steel Tubes for Low-Temperature Service
- A 369 Standard Specification for Carbon and Ferritic Alloy Steel Forged and Bored Pipe for High-Temperature Service
- API 5L Line Pipe
- 1 psi (lb/in2) = 6895 Pa (N/m2)
- 1000 psi = 6.9 MPa
- T (oC) = 5/9 (T (oF) - 32)
Example - Allowable Stress - 2000 psi vs. MPa
(20000 psi) (6895 Pa/psi) = 137900000 Pa
= 138 MPa
Low and Intermediate Alloy Steel Pipes and Tubes
- A 335 Seamless Ferritic Alloy Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service
- A 369 Carbon Steel and Ferritic Alloy Steel Forged and Bored Pipe for High-Temperature Service

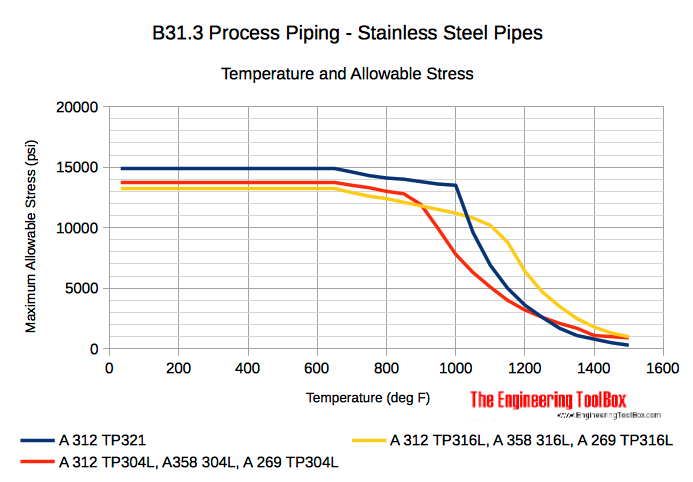
Seamless Austenitic Alloys Steel Pipes
- A 269 Seamless and Welded Austenitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service
- A 312 Seamless and Welded Austenitic Stainless Steel Pipe
- A 358 Electric-Fusion-Welded Austenitic Chromium-Nickel Alloy Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service
About B31.3 - Process Piping
B31.3 covers design of chemical and petroleum plants and refineries processing chemicals and hydrocarbons, water and steam. This Code contains rules for piping typically found in petroleum refineries; chemical, pharmaceutical, textile, paper, semiconductor, and cryogenic plants; and related processing plants and terminals.
This Code prescribes requirements for materials and components, design, fabrication, assembly, erection, examination, inspection, and testing of piping. This Code applies to piping for all fluids including: (1) raw, intermediate, and finished chemicals; (2) petroleum products; (3) gas, steam, air and water; (4) fluidized solids; (5) refrigerants; and (6) cryogenic fluids. Also included is piping which interconnects pieces or stages within a packaged equipment assembly.
B31.3 - Process Piping and Allowable Stress
For B31.3 Process piping, allowable stress is tensile strength at temperature divided by 3.
Note! for B31.1 - Power piping, allowable stress is tensile strength at temperature divided with 3.5.



