Miter Saw Angle Protractor – Quick & Accurate Angle Measurements
Use a miter saw angle protractor for precise angle calculations in woodworking and construction. Measure and cut perfect angles effortlessly.

The miter saw angles for cross cuts and decorative mouldings in corners or other locations can often be hard to measure correctly.
With this tool you measure the three lengths a, b and c as indicated in the drawing below. The miter saw cutting angles are easily calculated by inputting the values in the miter saw calculator below.
- Angle A (deg):
- Angle B (deg):
- Angle C (deg):
- Miter Saw Angle (deg):
- Skirting (Decorative Moulding) Saw Angle (deg):
The Skirting Saw Angle can be useful when cutting decorative mouldings, skirting boards and similar where the angle between the pieces are not 90 degrees and the cross cuts are not 45 degrees.
(enable pop-up)
Tip! - Distance c can be difficult to measure in corners. It may be helpful to use a stick or something similar with a known length for c. Position the stick somewhere in the corner as indicated in the drawings below. Measure the lengths a and b from the bottom of the corner to the ends of the stick.

Examples - Miter Saw Angle Calculator
The first example below with the default values used in the calculator above calculates the miter saw angle to 26.4 degrees for length a = 33.5, b = 40 and c = 39.1.
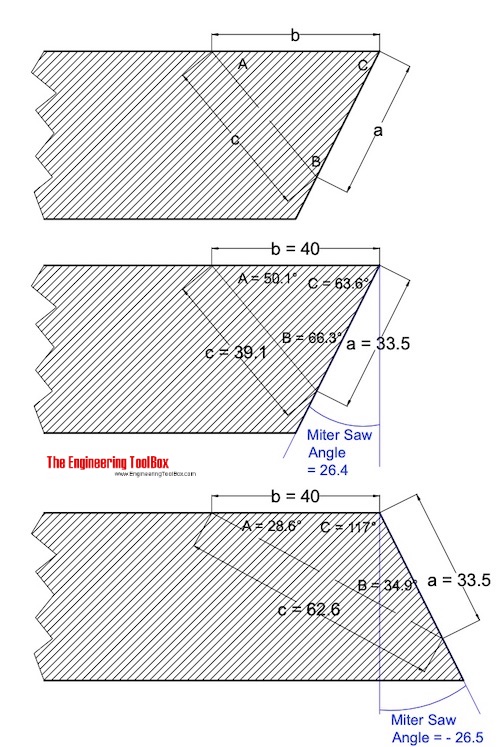
The second example calculates the miter saw angle to -26.5 degrees (miter saw opposite side compared to the first example) for lengths a = 33.5, b = 4 and c = 62.6.
Related Searches
miter saw • angle protractor • woodworking tools • miter cuts • angle measurement • construction tools • protractor guide • carpentry • DIY woodworking • saw angle calculator •



