Centroids of Plane Areas
The controid of square, rectangle, circle, semi-circle and right-angled triangle.
The centroid of an area is the point where the whole area is considered to be concentrated.
Square
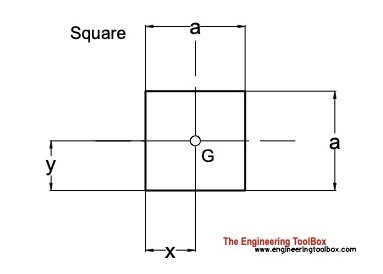
Distance
x = a / 2 (1a)
y = a / 2 (1b)
Area
A = a2 (1c)
Rectangle
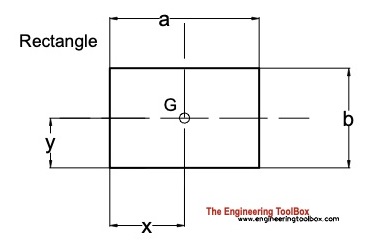
Distance
x = a / 2 (2a)
y = b / 2 (2b)
Area
A = a b (2c)
Circle
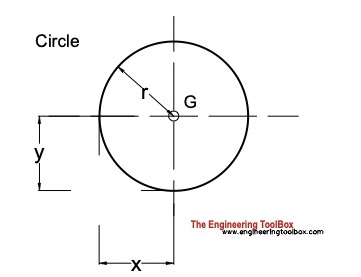
Distance
x = r (3a)
y = r (3b)
Area
A = π r2 (3c)
Semi-Circle
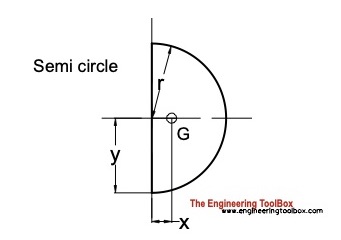
Distance
x = 4 r / (3 π) (4a)
y = r (4b)
Area
A = π r2/ 2 (4c)
Right-angled Triangle
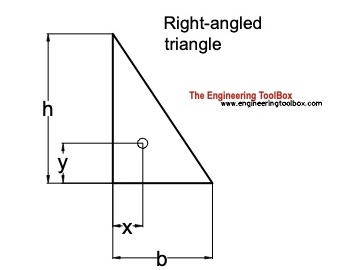
Distance
x = b / 3 (5a)
y = h / 3 (5b)
Area
A = b h / 2 (5c)



