Ducts Sizing - the Velocity Reduction Method
The velocity reduction method can be used when sizing air ducts.
The Velocity Reduction Method can be used when sizing air ducts. The method can be summarized to
- Select suitable velocities for main and branch ducts from the table below
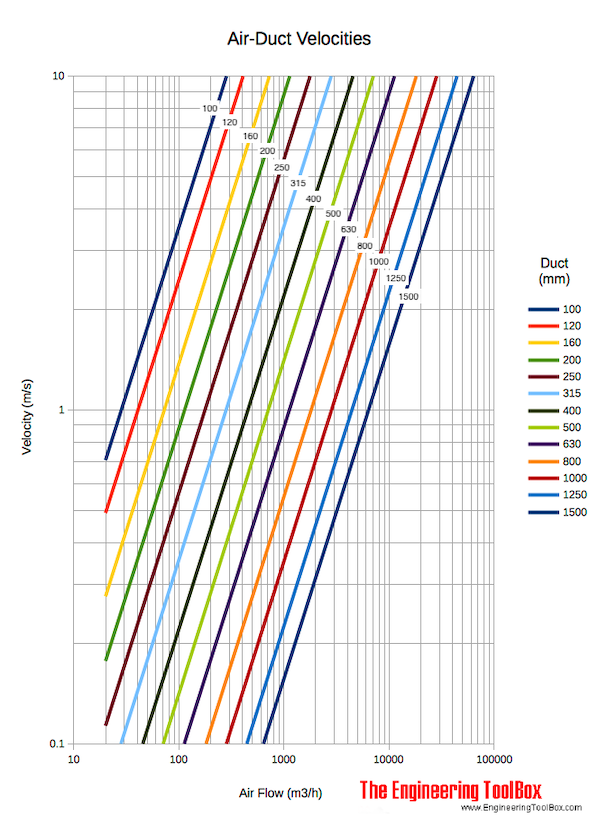
- Find the sizes of main and branch ducts from the air flow rates and the velocities by using eq. 1 and the charts below
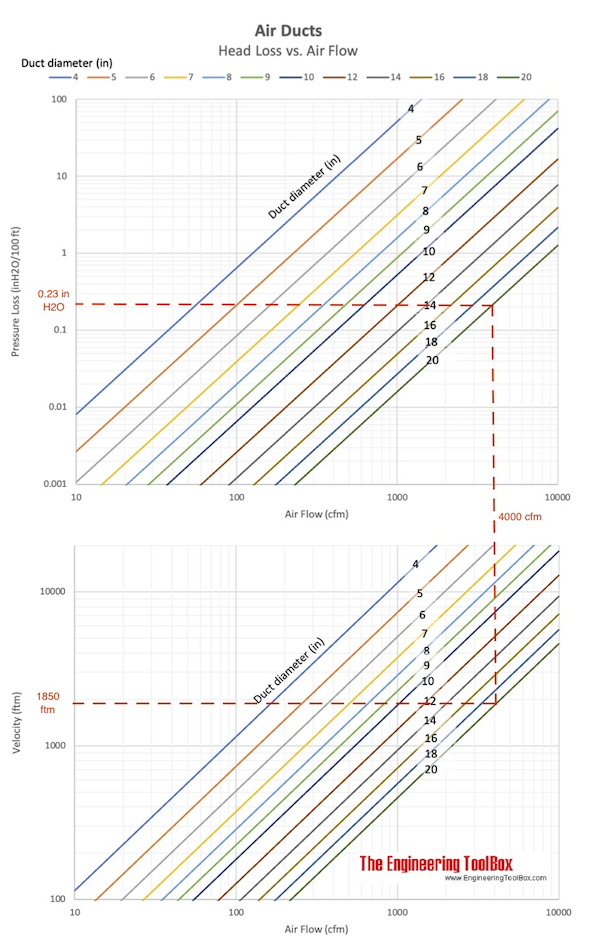
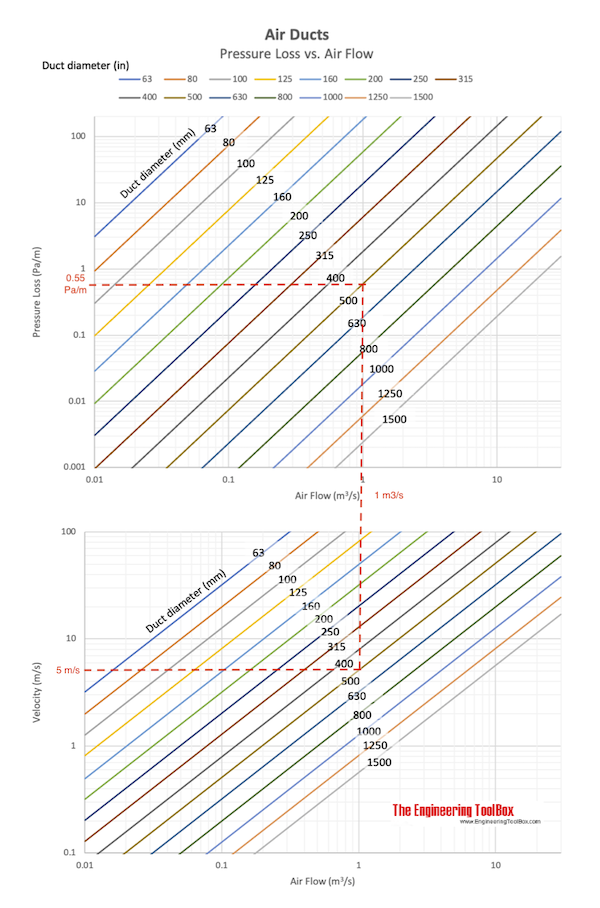
- From velocities and duct dimensions - find the frictional pressure loss in the main and branch ducts using the friction chart below
- Add minor dynamic loss
Proper Velocities
A proper velocity depends on application and environment. The table below indicate commonly used velocities:
| Type of Duct | Comfort Systems | Industrial Systems | High Speed Systems | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/s | ftm | m/s | ftm | m/s | ftm | |
| Main ducts | 4 - 7 | 780 - 1380 | 8 - 12 | 1575 - 2360 | 10 - 18 | 1670 - 3540 |
| Main branch ducts | 3 - 5 | 590 - 985 | 5 - 8 | 985 - 1575 | 6 - 12 | 1180 - 2360 |
| Branch ducts | 1 - 3 | 200 - 590 | 3 - 5 | 590 - 985 | 5 - 8 | 985 - 1575 |
Be aware that high velocity close to outlets and inlets may generate unacceptable noise.
Velocities commonly used for different applications:
- upstream medium pressure VAV boxes: 2000 to 2500 fpm (10 - 13 m/s)
- transport of fumes, mist or very light particulates: 2400 fpm (12 m/s)
- dust collection systems with small particulate: 3500 fpm (18 m/s)
- dust collection systems with heavy particulate like metals: 5000 fpm (25 m/s)
Sizing Ducts
Sizes of ducts are then given by the continuity equation like:
A = q / v (1)
where
A = duct cross sectional area (m2)
q = air flow rate (m3/s)
v= air speed (m/s)
Alternatively in Imperial units
Ai = 144 qi / vi (1b)
where
A = duct cross sectional area (sq.in.)
q = air flow rate (cfm)
v= air speed (fpm)
Frictional Pressure Loss
Estimate friction loss in main and branch ducts from the charts below:
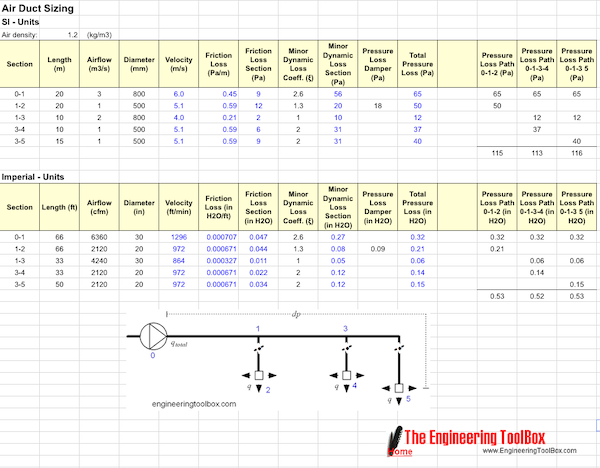
Air Ducts Sizing Spreadsheet Template
Air Ducts Spreadsheet Template - The Velocity Method
The velocity method can be done manual or more or less semi automatic with the spreadsheet template below.
open air duct sizing spreadsheet!
This template is based on the in the spreadsheet. Customize sections, airflows, duct sizes and minor dynamic loss coefficients - add pressure loss paths and evaluate and reconfigure the system to fit your criteria. Summarize pressure loss for each path and add damper pressure losses manually to balance the system.
The Google Docs spreadsheet template can be opened and copied here! The spreadsheet can also be downloaded as an excel file. Use the Google Docs "File" menu on the top of the template.