Duct Sizing - the Equal Friction Method
The equal friction method for sizing air ducts is easy and straightforward to use.
The equal friction method for sizing air ducts is often preferred because it is quite easy to use. The method can be summarized to
- Compute the necessary air volume flow (m3/s, cfm) in every room and branch of the system
- Use 1) to compute the total air volume (m3/s, cfm) in the main system
- Determine the maximum acceptable airflow velocity in the main duct
- Determine the major pressure drop in the main duct
- Use the major pressure drop for the main duct as a constant to determine the duct sizes throughout the distribution system
- Determine the total resistance in the duct system by multiplying the static resistance with the equivalent length of the longest run
- Compute balancing dampers
1. Compute the air volume in every room and branch
Use the actual heat, cooling or air quality requirements for the rooms and calculate required air volume flow - q.
2. Compute the total volume flow in the system
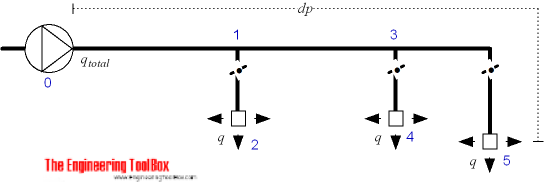
Make a simplified diagram of the system like the one above.
Use 1) to summarize and accumulate total air volume flow - qtotal - in the system.
Note! Be aware that maximum load conditions almost never occurs in all rooms at the same time. Avoid over-sizing the main system by multiplying the accumulated volume with a factor less than one (this is probably the hard part - and for larger systems sophisticated computer-assisted indoor climate calculations are often required).
3. Determine maximum acceptable airflow velocities in the main ducts
Determine maximum velocity in the main ducts on basis of application environment. To avoid unacceptable noise levels - keep maximum velocities within limits
- comfort systems - air velocity 4 to 7 m/s (13 to 23 ft/s)
- industrial systems - air velocity 8 to 12 m/s (26 to 40 ft/s)
- high speed systems - air velocity 10 to 18 m/s (33 to 60 ft/s)
Use maximum velocity limit when selecting size of main ducts.
4. Determine the static pressure drop in main duct
Use a pressure drop table or similar to determine static pressure drop in main duct.
5. Determine the duct sizes throughout the system
Use the static pressure drop from 4) as a constant to determine the ducts sizes throughout the system. Use the air volumes calculated in 1) for the calculation. Select the duct sizes with the pressure drop for the actual ducts as close to the main duct pressure drop as possible.
6. Determine the total resistance in the system
Use the static pressure from 4) to calculate the pressure drop through the longest part of the duct system. Add minor loss by using equivalent lengths or minor loss coefficients as used in the example spreadsheet below.
7. Calculate balancing dampers
Use the total resistance in 6) and the volume flow throughout the system to calculate dampers and their theoretical pressure loss.
Note about the Equal Friction Method
The equal friction method is straightforward and easy to use and gives an automatic reduction of air flow velocities through the system. The reduced velocities are in general within the noise limits of the application environment.
Typical values used for friction loss are 0.1 in H2O/100 ft (0.85 Pa/m) for supply ducts and 0.08 in H2O/100 ft (0.65 Pa/m) for return ducts.
The method can increase the numbers of reductions compared to other methods and often a poorer pressure balance in the system require more adjusting dampers. This may increase the system cost compared to other methods.
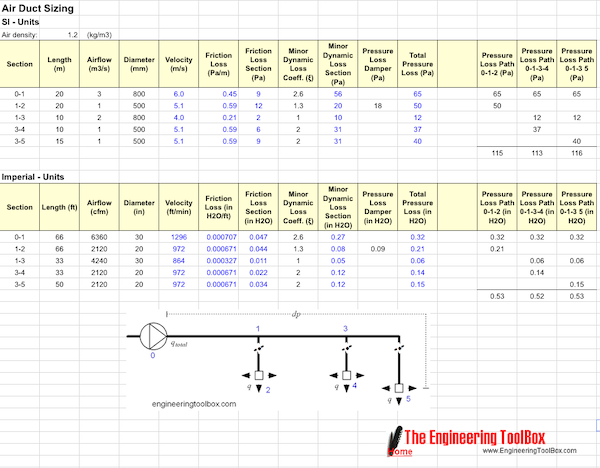
Example Template - The Equal Friction Method
The equal friction method can be done manual or more or less semi automatic with the spreadsheet template below.
This template is based on the figure above. Customize sections, airflows, duct sizes and minor dynamic loss coefficients - add pressure loss paths and evaluate and reconfigure the system to fit your criteria. Summarize pressure loss for each path and add damper pressure losses manually to balance the system.
The Google Docs spreadsheet template can be opened and copied here! The spreadsheet can also be downloaded as an excel file. Use the Google Docs "File" menu on the top of the template.