Noise generated in Air Ducts
Estimate noise generated by air flow in ducts.
Air flow in ducts generates noise. The noise in the duct is determined by
- air velocity
- duct size (cross sectional area)
Generated noise can be calculated with the empirical equation
LN = 10 + 50 log(v) + 10 log(A) (1)
where
LN = sound power level in the duct (dB)
v = air velocity (m/s)
A = air duct cross sectional area (m2)
The equation modified for imperial units
LN = 10 + 50 log(vi / 197) + 10 log(Ai / 1550) (1b)
where
vi = air velocity (ft/min)
Ai = cross sectional area (in2)
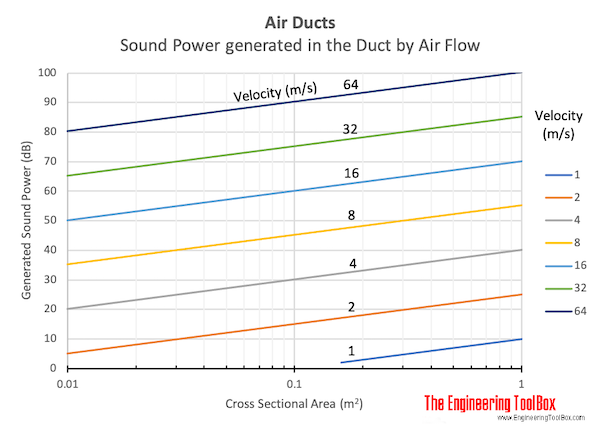
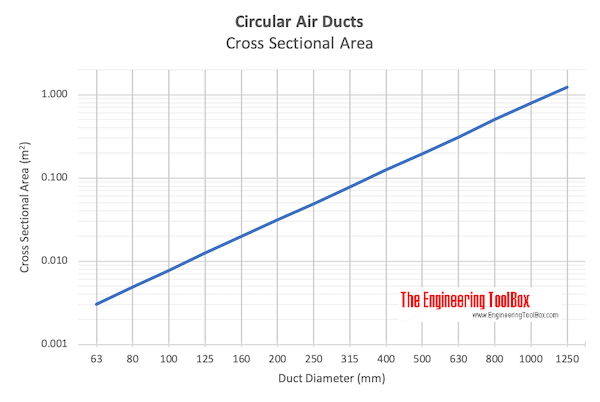
Example - Generated Noise in Duct by Air Flow
The cross section area of a 200 mm duct can be calculated as
A = π ((0.2 m) / 2)2)
= 0.0314 m2
The noise generated in the duct with an air flow velocity 10 m/s can be calculated as
LN = 10 + 50 log(10 m/s) + 10 log(0.0314 m2)
= 45 db
The noise generated in the same 200 mm circular duct as above with air flow velocity 20 m/s can be calculated as
LN = 10 + 50 log(20 m/s) + 10 log(π ((0.2 m) / 2)2)
= 60 db
Note! - due to the noise generated by fans - noise generated inside ducts by air flow can in general be neglected.



