Belts - Pulley Diameters vs. Speed
The pulley laws - driver and driven - diameter and rpm
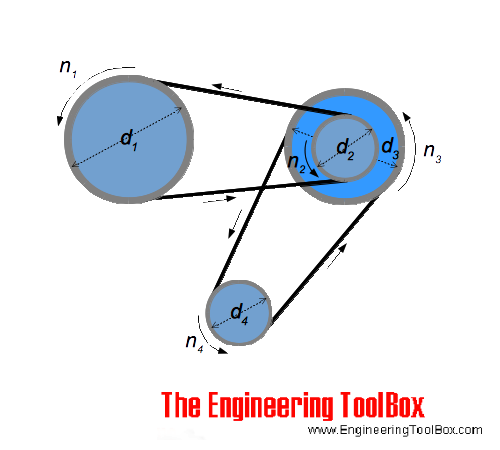
Pulleys - Speed vs. Pulley Diameters
| Pulley | Diameter (mm, in) | Speed (rpm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
Single Belt Transmission - one driving pulley and one driven pulley
For a system with two shafts and two pulleys - as indicated with pulley 1 and 2 in the figure above:
d1 n1= d2 n2 (1)
where
d1 = driving pulley diameter (inch, mm)
n1 = revolutions of driving pulley (rpm - rounds per minute)
d2 = driven pulley diameter (inch, mm)
n2 = revolutions of driven pulley (rpm - rounds per minute)
Equation (1) can be transformed to express the
Revolution of Driven Pulley
n2 = d1 n1 / d2 (2)
Revolution of Driver Pulley
n1 = d2 n2 / d1 (3)
Diameter of Driven Pulley
d2 = d1 n1 / n2 (4)
Diameter of Driver Pulley
d1 = d2 n2 / n1 (5)
Multiple Belt Transmission Systems
For a system a with three shafts and four pulleys - as indicated in the figure above:
n2 = n3 (6)
n4 = n1 (d1 d3) / (d2 d4) (7)
Example - Multiple Belt Transmission System
The revolutions of shaft 4 in a multiple belt transmission like indicated in the figure above where
n1 = 1000 rpm
d1 = 100 mm
d2 = 50 mm
d3 = 110 mm
d4 = 60 mm
can be calculated as
n4 =(1000 rpm) (100 mm) (110 mm) / ((50 mm) (60 mm))
= 3667 rpm



