Fan Affinity Laws
The affinity laws can be used to calculate resulting volume capacity, head or power consumption when speed or wheel diameters are changed.
The Affinity Laws for centrifugal pumps and fans are used to express the influence on volume capacity, head (pressure) and/or power consumption due to
- change in wheel speed - revolutions per minute (rpm), and/or
- geometrically similarity by change in impeller diameter
Note that the affinity laws for pumps are not identical with fans.
Fan Affinity Laws
Volume Flow Capacity
The volume flow capacity of a centrifugal fan can be expressed as
q1 / q2 = (n1 / n2) (d1 / d2)3 (1)
where
q = volume flow capacity (m3/s, gpm, cfm, ..)
n = wheel velocity - revolution per minute - (rpm)
d = wheel diameter
Head or Pressure
The head or pressure of a centrifugal fan can be expressed as
dp1 / dp2 = (n1 / n2)2 (d1 / d2)2 (2)
where
dp = head or pressure (m, ft, Pa, psi, ..)
Power
The power consumption of a centrifugal fan can be expressed as
P1 / P2 = (n1 / n2)3 (d1 / d2)5 (3)
where
P = power (W, bhp, ..)
Changing the Wheel Velocity
If the wheel diameter is constant - the affinity laws for change in wheel velocity can be simplified to
Volume Flow Capacity
q1 / q2 = (n1 / n2) (1a)
Head or Pressure
dp1 / dp2 = (n1 / n2)2 (2a)
Power
P1 / P2 = (n1 / n2)3 (3a)
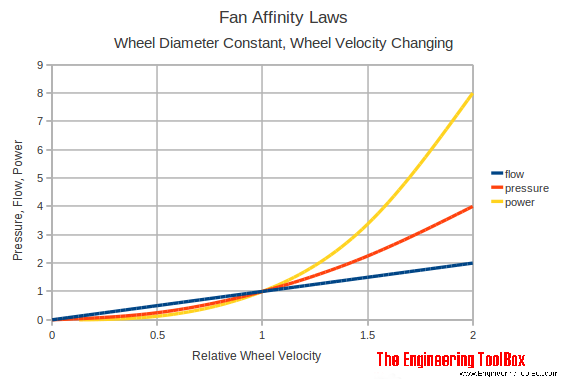
Note! - if the speed of a fan is increased with 10%
- the volume flow is increased with 10%
- the head is increased with 21%
- the power is increased with 33 %
- if the volume flow capacity of an existing system is increased with 10% - the power supply increases with 33% and the electrical motor and the power supply may need an upgrade.
Fan Affinity Laws Calculator - Changing Wheel Velocity
Replace the default values with the actual values. The calculator is generic and can be used with all common units as long as the units use is consistent.
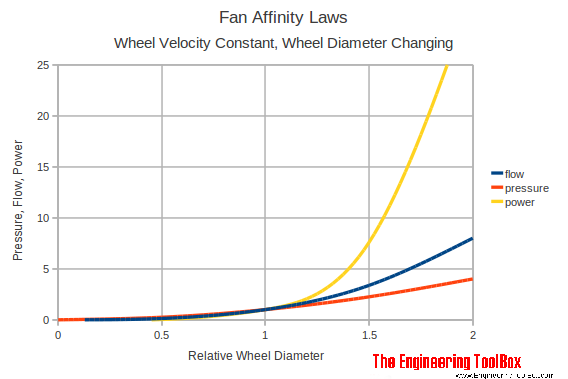
Changing the Impeller Diameter
If the wheel velocity is constant - the affinity laws for change in impeller diameter can be simplified to
Volume Capacity
q1 / q2 = (d1 / d2)3 (1b)
Head or Pressure
dp1 / dp2 = (d1 / d2)2 (2b)
Power
P1 / P2 = (d1 / d2)5 (3b)
Fan Affinity Laws Calculator - Changing Wheel Diameter
Replace the default values with the actual values. The calculator is generic and can be used with all common units as long as the use is consistent.
Equivalent Static Pressure
Use of the fan laws can sometimes be simplified by using Equivalent Static Pressure - ESP - defined as the pressure that would be developed by a fan operating at standard air density instead of the actual air density.
ESP = dpact ρstd / ρact (4)
where
ESP = Equivalent Static Pressure (Pa)
dpact = actual pressure (Pa)
ρstd = standard density of air (kg/m3)
ρact = actual density of air (kg/m3)
ESP can be useful when selecting fans from published data based on standard conditions.



