Sound - Attenuation and the Directivity Coefficient
The attenuation in a room depends on the location of the sound source and the receiver - and the room constant.
For a continuing sound source the sound level in a room is the sum of direct and reverberant sound. The sound pressure for a receiver can be expressed as
Lp = LN + log(D / (4 π r2) + 4 / R) (1)
where
Lp = received sound pressure level (dB)
LN = sound power level from source (dB)
D = directivity coefficient
R = room constant (m2 Sabine)
π = 3.14 .....
r = distance from source (m)
Directivity coefficient - D
The figure below can be used to approximate the Directivity coefficient - D - for typical locations of the receiver and the sound source
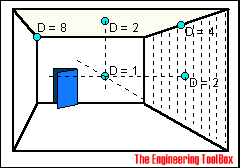
(1) can be transformed to express the difference between the received sound pressure level and emitted sound power level - the attenuation - as:
Lp - LN = 10 log(D / (4 π r2) + 4 / R) (2)
Room Sound Attenuation Calculator
The attenuation (Lp - LN) can also be estimated from the diagram below by modifying (2) to be expressed as the ratio between "distance r between source and receiver" and "square of the directivity coefficient D" - and the total room sound absorption in m2 Sabine.
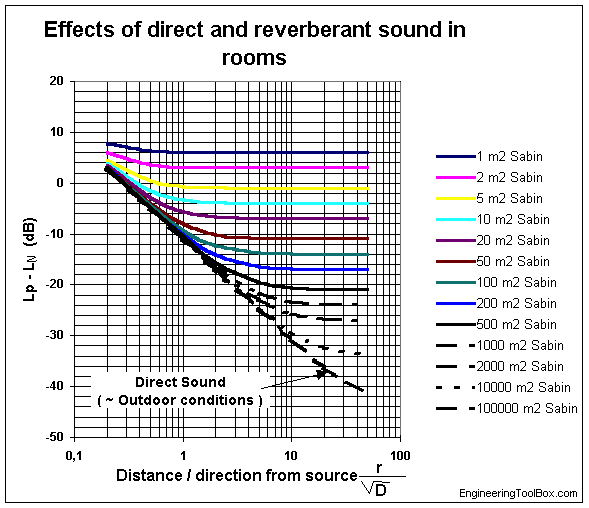
Example - Sound Attenuation in a Room
For a room the acoustic property total room sound absorption is 1000 m2 Sabine. For a listener in the middle of the room with a directivity constant 1 and at distance 1 m from the sound source - the ratio
r / D1/2 = 1 / (1 m)1/2
= 1
From the diagram above the attenuation can estimated to approximately
10 dB



