Condensate Generated in Cold Steam Pipes - SI Units
Huge amounts of condensate are generated when cold steam pipes are heated up must be drained from the pipes.
When cold steam pipes are heated up huge amounts of condensate are generated and must be drained from the pipes. It is important that steam traps are designed to handle start-up loads.
The diagram and table below can be used to roughly estimate the load of warm-up condensate generated when a steam system is heated up.
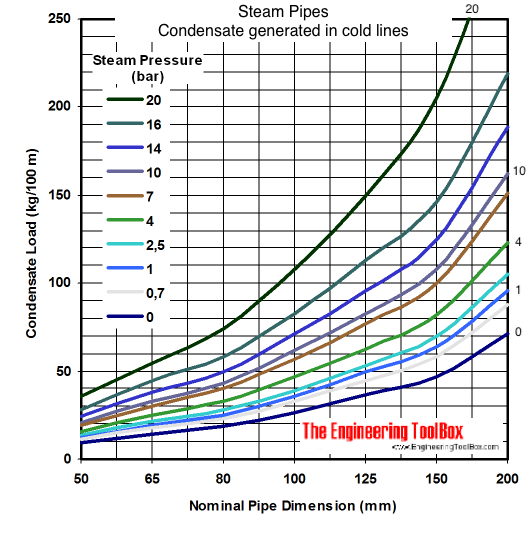
For full table - rotate the screen!
| Steam Pressure (bar) | Condensate Generation (kg/100 m) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal Pipe Dimension (mm) | ||||||||||||||
| 50 | 65 | 80 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | 600 | |
| 0 | 9.2 | 14.4 | 19 | 27 | 37 | 47 | 71 | 101 | 134 | 159 | 208 | 262 | 308 | 309 |
| 0.35 | 10 | 15.9 | 20.8 | 29 | 40 | 52 | 69 | 112 | 146 | 174 | 227 | 287 | 338 | 470 |
| 0.7 | 11.3 | 17.8 | 23.4 | 33 | 45 | 58 | 88 | 125 | 165 | 196 | 255 | 322 | 379 | 529 |
| 1 | 12.2 | 19.5 | 25.4 | 36 | 50 | 64 | 96 | 135 | 179 | 212 | 277 | 350 | 412 | 575 |
| 2.5 | 13.4 | 21.3 | 27.8 | 39 | 53 | 70 | 105 | 148 | 195 | 232 | 303 | 383 | 450 | 627 |
| 4 | 15.8 | 25.2 | 33 | 47 | 63 | 82 | 123 | 175 | 233 | 276 | 360 | 454 | 535 | 745 |
| 5.5 | 17.8 | 28 | 37 | 52 | 71 | 92 | 138 | 196 | 260 | 308 | 402 | 507 | 598 | 832 |
| 7 | 19.3 | 30.6 | 40 | 57 | 77 | 100 | 151 | 214 | 284 | 335 | 438 | 553 | 651 | 906 |
| 8.5 | 20.1 | 31.8 | 42 | 59 | 80 | 104 | 157 | 223 | 293 | 349 | 455 | 574 | 676 | 942 |
| 10 | 20.8 | 33.1 | 43 | 62 | 83 | 108 | 162 | 230 | 305 | 361 | 472 | 595 | 700 | 997 |
| 12 | 22.6 | 35.8 | 47 | 67 | 90 | 117 | 176 | 250 | 331 | 392 | 513 | 646 | 760 | 1059 |
| 14 | 24.2 | 38.2 | 50 | 71 | 96 | 125 | 189 | 267 | 353 | 418 | 546 | 689 | 811 | 1130 |
| 16 | 28.1 | 45 | 58 | 83 | 113 | 146 | 219 | 312 | 412 | 489 | 638 | 805 | 947 | 1320 |
| 20 | 36 | 55 | 74 | 108 | 150 | 205 | 312 | 463 | 637 | 764 | 981 | 1228 | 1503 | 1700 |
| 25 | 39 | 59 | 80 | 117 | 162 | 222 | 338 | 502 | 692 | 828 | 1065 | 1362 | 1631 | 2315 |
| 30 | 41.5 | 64 | 85 | 124 | 173 | 237 | 360 | 534 | 735 | 882 | 1134 | 1420 | 1763 | 2464 |
| 40 | 44.3 | 68 | 91 | 132 | 184 | 253 | 385 | 570 | 784 | 940 | 1210 | 1514 | 1852 | 2627 |



