Substances Triple Points
Triple points for common substances.
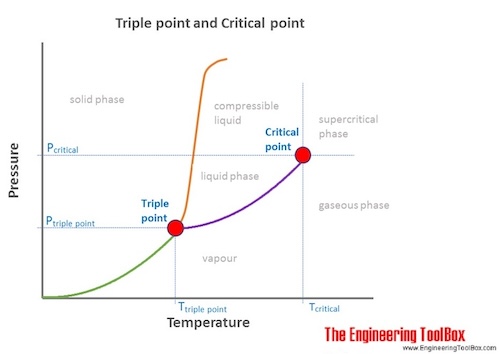
Triple point: The combination of the temperature and the pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of a substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
Triple point for some common substances:
See also Critical Temperatures and Pressures for some common substances
| Substance | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (kPa) |
|---|---|---|
| Acetylene | -80.7 | 120 |
| Air | -213.40 | 5.265 |
| Ammonia | -77.75 | 6.076 |
| Argon | -189.34 | 68.9 |
| Arsenic | 820 | 3628 |
| Butane | -138.6 | 0.0007 |
| Carbon (graphite) | 4492 | 10132 |
| Carbon dioxide | -56.60 | 517 |
| Carbon monoxide | -205.05 | 15.37 |
| Chloroform | -97.72 | 0.870 |
| Deuterium | -254.52 | 17.1 |
| Ethane | -183.26 | 0.0008 |
| Ethanol | -123 | 0.00000043 |
| Ethylene | -169.2 | 0.12 |
| Formic acid | 8.25 | 2.2 |
| Hexafluoroethane | -100.07 | 26.60 |
| Hydrogen | -259.31 | 7.04 |
| Hydrogen chloride | -114.19 | 13.9 |
| Iodine | 113.50 | 12.07 |
| Isobutane | -159.60 | 0.000019481 |
| Krypton | -157.39 | 74.12 |
| Mercury | -39.0 | 0.000000165 |
| Methane | -182.47 | 11.7 |
| Neon | -248.58 | 43.2 |
| Nitric oxide | -163.65 | 21.92 |
| Nitrogen | -209.97 | 12.6 |
| Nitrous oxide | -90.81 | 87.85 |
| Oxygen | -218.79 | 0.152 |
| Palladium | 1552 | 0.0035 |
| Platinum | 1772 | 0.00020 |
| Radon | -71 | 70 |
| Sulfur dioxide | -75.46 | 1.67 |
| Titanium | 1668 | 0.0053 |
| Uranium hexafluoride | 64.02 | 151.7 |
| Water | 0.01 | 0.611657 |
| Xenon | -111.8 | 81.5 |
| Zinc | 419.50 | 0.065 |
- 1 kPa (103 Pa) = 0.145 psi
The triple point is not the same as the critical point.



