Relative vs. Absolute Voltage
Electric circuits and voltage at any point.
Absolute Voltage
If voltage at point A is quoted with reference to the earth point - the absolute potential - then the voltage is written UA.
Relative Voltage
If voltage at point A is quoted with reference to point B - then the voltage is written UAB.
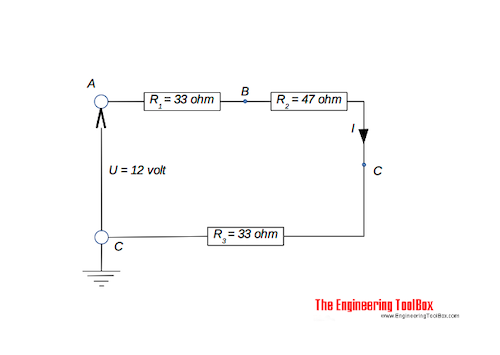
Example - Relative and Absolute Voltage
The total resistance in the series circuit above can be calculated
R = (33 ohm) + (47 ohm) + (33 ohm)
= 113 ohm
The current in the circuit can be calculated
I = (12 volts) / (113 ohm)
= 0.11 ampere
The relative voltage between point A and B - VAB - can be calculated
UAB = (33 ohm) (0.11 ampere)
= 3.6 volts
The absolute voltage in point A relative to earth is
UA = 12 V
The absolute voltage in point B relative to earth is
UB = UA - UAB
= (12 volt) - (3.6 volt)
= 8.4 volt



