Radiation Heat Transfer
Heat transfer due to emission of electromagnetic waves is known as thermal radiation.
Heat transfer through radiation takes place in form of electromagnetic waves mainly in the infrared region. Radiation emitted by a body is a consequence of thermal agitation of its composing molecules. Radiation heat transfer can be described by reference to the 'black body'.
The Black Body
The black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on its surface. Actual black bodies don't exist in nature - though its characteristics are approximated by a hole in a box filled with highly absorptive material. The emission spectrum of such a black body was first fully described by Max Planck.
A black body is a hypothetical body that completely absorbs all wavelengths of thermal radiation incident on it. Such bodies do not reflect light, and therefore appear black if their temperatures are low enough so as not to be self-luminous. All black bodies heated to a given temperature emit thermal radiation.
The radiation energy per unit time from a black body is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature and can be expressed with the Stefan-Boltzmann Law as
q = σ T4 A (1)
where
q = heat transfer per unit time (W)
σ = 5.6703×10-8 (W/m2K4) - The Stefan-Boltzmann Constant
T = absolute temperature in kelvins (K)
A = area of the emitting body (m2)
The Stefan-Boltzmann Constant in Imperial Units
σ = 5.6703×10-8 (W/m2K4)
= 1.714×10-9 ( Btu/(h ft2 oR4))
= 1.19×10-11 ( Btu/(h in2 oR4))
Example - Heat Radiation from the surface of the Sun
If the surface temperature of the sun is 5800 K and if we assume that the sun can be regarded as a black body the radiation energy per unit area can be expressed by modifying (1) to
q / A = σ T4
= (5.6703×10-8 W/m2K4) (5800 K)4
= 6.42 107 (W/m2)
Gray Bodies and Emissivity Coefficients
For objects other than ideal black bodies ('gray bodies') the Stefan-Boltzmann Law can be expressed as
q = ε σ T4 A (2)
where
ε = emissivity coefficient of the object (one - 1 - for a black body)
For the gray body the incident radiation (also called irradiation) is partly reflected, absorbed or transmitted.
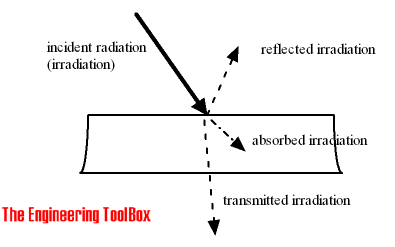
The emissivity coefficient is in the range 0 < ε < 1, depending on the type of material and the temperature of the surface.
- oxidized Iron at 390 oF (199 oC) > ε = 0.64
- polished Copper at 100 oF (38 oC) > ε = 0.03
- emissivity coefficients for some common materials
Net Radiation Loss Rate
If an hot object is radiating energy to its cooler surroundings the net radiation heat loss rate can be expressed as
q = ε σ (Th4 - Tc4) Ah (3)
where
Th= hot body absolute temperature (K)
Tc= cold surroundings absolute temperature (K)
Ah = area of the hot object (m2)
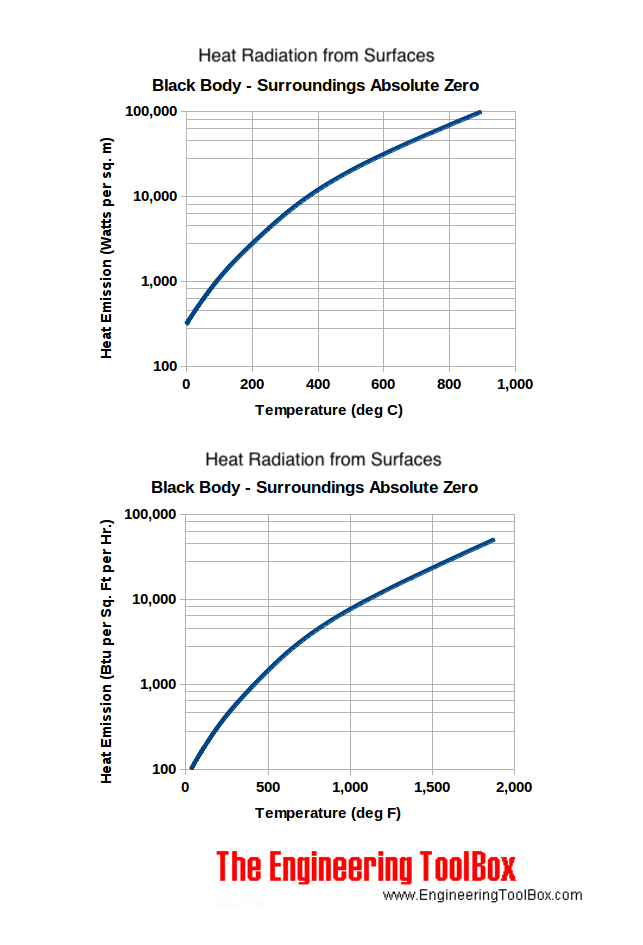
Heat loss from a heated surface to unheated surroundings with mean radiant temperatures are indicated in the chart below.
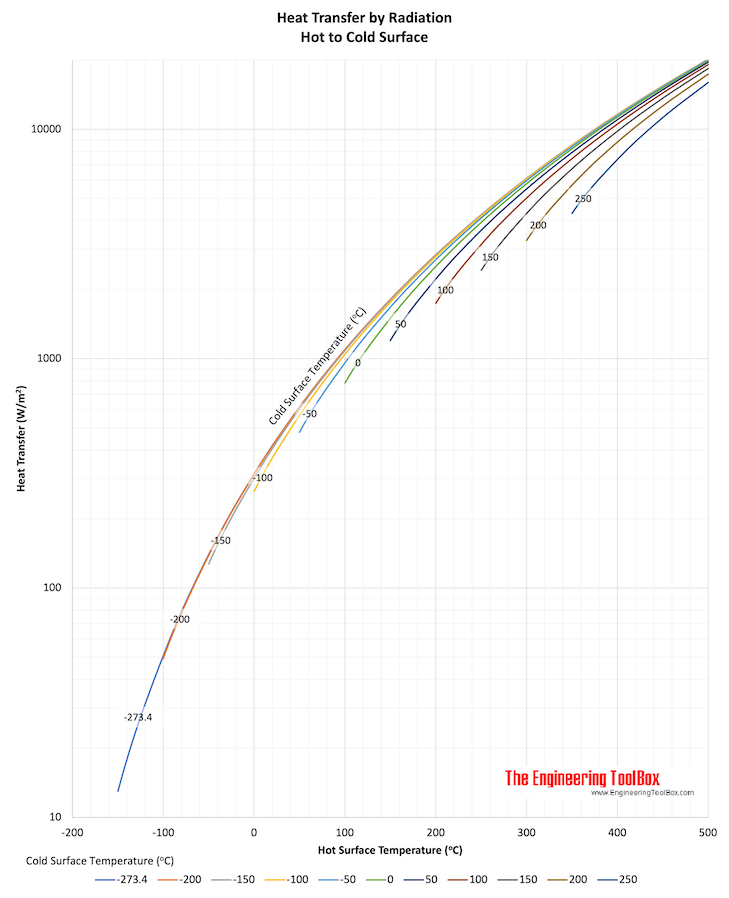
Download and print Heat Transfer by Radiation chart
Radiation Heat Transfer Calculator
This calculator is based on equation (3) and can be used to calculate the heat radiation from a warm object to colder surroundings.
Note that the input temperatures are in degrees Celsius.
Lambert's cosine law
Heat emission from a surface in an angle β can be expressed with Lambert's cosine law as
qβ = q cos(β) (4)
where
qβ = heat emission in angle β
q = heat emission from the surface
β = angle