Electrical Parallel Circuits
Resistance, voltage and current in electrical parallel circuits.
In a parallel circuit there is more than one path the electrons can flow.
The Parallel Circuit Rules:
- The total current in parallel circuit is equal to the sum of the currents in all the branches of the circuit.
- The total voltage across a parallel circuit is equal to the voltage across any of the branches in the circuit.
- The total resistance of a parallel circuit is calculated by using Ohm's law on the voltage and current of the whole circuit.
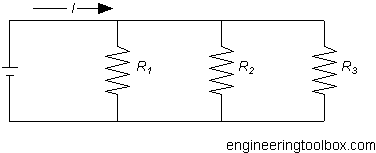
The sum of currents in a parallel network can be calculated as
I = I1 + I2 + ... + In (1)
where
In = parallel current (amps)
I = sum of currents (amps)
The total resistance in a parallel circuit can be calculated as
1 / R = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 + ... + 1 / Rn (2)
where
Rn = parallel resistance (ohms, Ω)
R = total resistance in the parallel network (ohms, Ω)
Example - Parallel Network
The total resistance in a network with three resistors R1 = 10 Ω, R2= 20 Ω and R3 = 30 Ω can be calculated as
1 / R = 1 / (10 Ω) + 1 / (20 Ω) + 1 / (30 Ω)
= 0.183 (1/Ω)
R = 1 / 0.183
= 5.46 Ω
Connected to a 12 V battery the sum of currents can be calculated
I = U / R
= (12 V) / (5.46 Ω)
= 2.2 amps
The current through each resistor can be calculated as
I1 = U / R1
= (12 V) / (10 Ω)
= 1.2 amps
I2= U / R2
= (12 V) / (20 Ω)
= 0.6 amps
I3 = U / R3
= (12 V) / (30 Ω)
= 0.4 amps
Resistors in Parallel and resulting Resistance
Two resistors in parallel - resistance ranging 1 - 100 ohm
| R2 (Ω) |
Resulting Resistance (Ω) | |||||||||||
| R1 (Ω) | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 3.3 | 4.7 | 6.8 | 10 | 15 | 22 | 33 | 47 | 68 | |
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.75 | 0.89 | 1.03 | 1.14 | 1.22 | 1.30 | 1.36 | 1.40 | 1.43 | 1.45 | 1.46 |
| 2.2 | 0.69 | 0.89 | 1.1 | 1.32 | 1.50 | 1.66 | 1.82 | 1.92 | 2.0 | 2.06 | 2.10 | 2.13 |
| 3.3 | 0.77 | 1.03 | 1.32 | 1.65 | 1.94 | 2.22 | 2.48 | 2.70 | 2.87 | 3.00 | 3.08 | 3.14 |
| 4.7 | 0.83 | 1.14 | 1.50 | 1.94 | 2.35 | 2.78 | 3.20 | 3.58 | 3.87 | 4.12 | 4.27 | 4.39 |
| 6.8 | 0.87 | 1.22 | 1.66 | 2.22 | 2.78 | 3.40 | 4.05 | 4.68 | 5.19 | 5.64 | 5.94 | 6.18 |
| 10 | 0.91 | 1.30 | 1.82 | 2.48 | 3.20 | 4.05 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 6.9 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 8.7 |
| 15 | 0.93 | 1.36 | 1.92 | 2.70 | 3.58 | 4.68 | 6.0 | 7.50 | 8.9 | 10.3 | 11.4 | 12.2 |
| 22 | 0.95 | 1.40 | 2.00 | 2.87 | 3.87 | 5.19 | 6.9 | 8.9 | 11.0 | 13.2 | 15.0 | 16.6 |
| 33 | 0.97 | 1.43 | 2.06 | 3.0 | 4.12 | 5.64 | 7.7 | 10.3 | 13.2 | 16.5 | 19.4 | 22.2 |
| 47 | 0.98 | 1.45 | 2.1 | 3.08 | 4.27 | 5.94 | 8.3 | 11.4 | 15.0 | 19.4 | 23.5 | 27.8 |
| 68 | 0.99 | 1.46 | 2.13 | 3.14 | 4.39 | 6.18 | 8.7 | 12.2 | 16.6 | 22.2 | 27.8 | 34.0 |




