Movement Ratio
Machines and movement ratio (velocity ratio).
A machine is a device that can change the magnitude and line of action of a force.
Examples are
- pulley systems
- gear systems
- screw-jacks
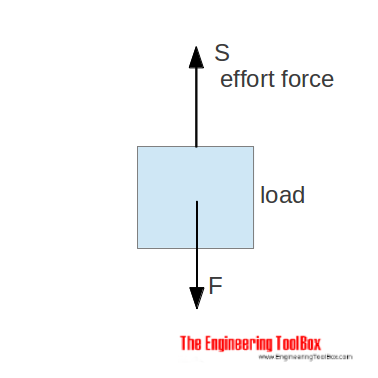
A simple machine amplifies the input force (effort) to a larger output force (load).
Movement Ratio
The movement ratio (or velocity ratio) of a machine is defined as the ratio of the distance moved by the effort to the distance moved by the load. Movement ratio can be expressed as
Mr = se / sl
= velocity ratio (1)
where
Mr = movement ratio
se = distance moved by the effort (m, ft)
sl = distance moved by the load (m, ft)
Machine Efficiency
The efficiency of a simple machine is defined as the ratio of the force ratio to the movement ratio and can be expressed as
μ = Fr / Mr (2)
where
μ = machine efficiency
Fr = force ratio



