Hot Water Circulation System - Return Pipes
Hot water can be circulated through a return pipe if it's instantly required at the fixtures.
A return circulation pipe is sometimes provided in a hot-water system where it is desirable to have hot water available continuously at the fixtures. Typically for systems where the distance from the hot water heater to the consumption fixtures exceeds 25 - 30 m.
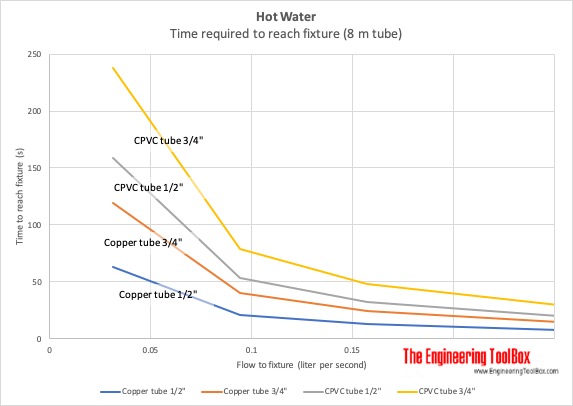
Time for Hot Water to reach Fixture without Circulation Pump
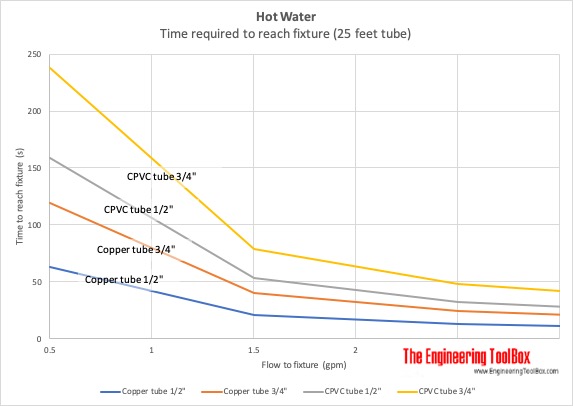
- 1 U.S. gpm = 0.0630 liter/sec
- 1 feet = 0.305 m
Hot Water Circulation Pump
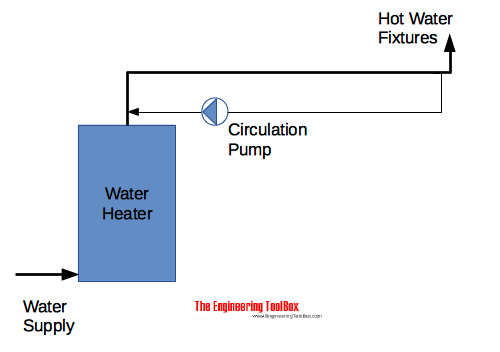
A smaller pipe with an inline pump is connected to a point close to the most distant fixture and to a point close to the hot water heater. The pump can run continuously or intermittent circulating enough water to keep the temperature drop in the pipeline during low or no consumption within an acceptable limit.
The required circulated water flow can be calculated
Q = q / (ρ cp dt) (1)
where
Q = pump capacity (m3/s)
q = heat loss from the pipe line (W)
ρ = density of water (kg/m3) (988 kg/m3 at 50 oC)
cp = specific heat of water (J/kgoC) (4182 J/kgoC at 50 oC)
dt = temperature drop (oC)
Typical heat loss from an insulated pipe line is in the range 30 - 60 W/m. Acceptable temperature drop can be 10 oC.
Example - Required Circulation Volume in a Hot Water Return Pipe Line
The length of a pipeline inclusive the circulation line is 100 m. With water at temperature 50 oC the average specific heat loss from the pipe line is estimated to 30 W/m. The total heat loss from the whole pipe line can be calculated as
q = (100 m) (30 W/m)
= 3000 W
Required water flow to limit the temperature drop to 10 oC can be calculated as
Q = (3000 W) / ((988 kg/m3) (4182 J/kgoC) (10 oC))
= 7.2×10-5 m3/s
= (7.2×10-5 m3/s) (1000 liter/m3)
= 0.072 liter/s