Floor Vibrations
Human activities like walking, running and dancing - and operating machines - can introduce floor vibrations due to resonance.
Human activities like walking, dancing or running may generate frequency acting forces in a construction.
The frequencies are in general in the range 1.0 to 3.0 Hz (1/s) - normally below the most common resonance frequencies for floor constructions.
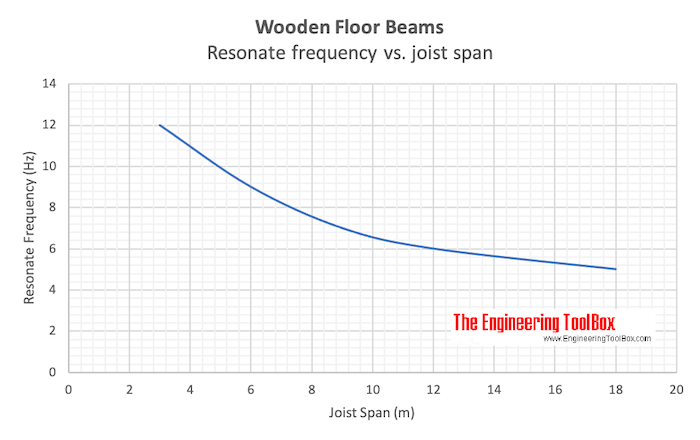
Typical resonate frequencies in wooden beam floors are
- Joist span 3 m : 12 Hz
- Joist span 6 m : 9 Hz
- Joist span 9 m : 7 Hz
- Joist span 12 m : 6 Hz
- Joist span 18 m : 5 Hz
Resonate frequencies in concrete floors on the ground depends on the materials in the ground below. Typical resonate frequencies ranges 10 - 100 Hz:
- Sand : 15 - 25 Hz
- Clay, wet : 15 Hz
- Clay, hard : 30 Hz
- Gravel : 20 - 25 Hz
- Limestone : 35 - 45 Hz
- Solid rock : 40 - 50 Hz
Example - Running Cadence
The force frequency - f - for a "everyday" runner with cadence 150 steps pr. minute can be calculated
f = (150 1/min) (1 / 60 min/s)
= 2.5 (1/s, Hz)
The force frequency - f - for a "elite" runner with cadence 200 steps pr. minute can be calculated
f = (200 1/min) (1 / 60 min/s)
= 3.3 (1/s, Hz)



