Elevators - Force and Power
Required force and power to lift an elevator.
Work done by Lifting the Elevator
The work done by lifting an elevator from one level to an other can be expressed as
W = m ag (h1 - h0) (1)
where
W = work done (J, ft lbf)
m = mass of elevator and passengers (kg, lbm)
ag = acceleration of gravity (9.81 m/s2, 32.17 ft/s2)
h1 = final elevation (m, ft)
h0 = initial elevation (m, ft)
The generic equation for work done by a force can be expressed as
W = Fc s (2)
where
W = work done by force (J, ft lbf)
Fc = force acting on the elevator at constant speed (N, lbf)
s = distance moved by elevator (m, ft)
Forces acting on the Elevator
Since works done in (1) and (2) are equal - the equations can be combined to
Fc s = m ag (h1 - h0) (3)
Force at constant Speed
Since the difference in elevation and the distance moved by the force are equal - (3) can be modified to express the force required to move the elevator at constant speed to
Fc = m ag (4)
Force at start/stop
When the elevator starts or stops - the acceleration or deceleration force in addition to the constant speed force can be expressed as
Fa = m (v1 - v0) / ta (5)
where
Fa = acceleration force (N, lbf)
v1 = final velocity (m/s, ft/s)
v0 = initial velocity (m/s, ft/s)
ta = start or stop (acceleration) time (s)
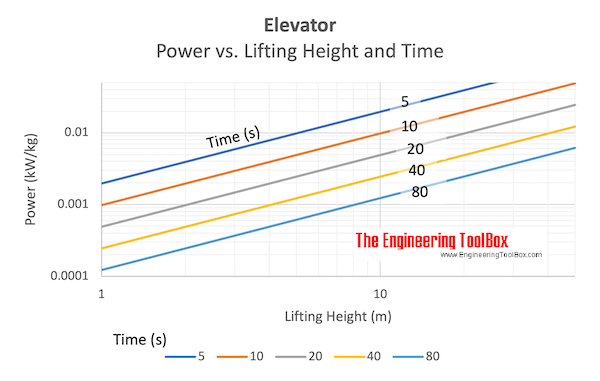
Power required to move the Elevator
The power required to move the elevator can be calculated as
P = W / t
= m ag (h1 - h0) / t (6)
where
P = power (W, ft lbf)
t = time to move the elevator between levels (s)
Example - Force and Power to Lift an Elevator
An elevator with mass 2000 kg including passengers are moved from level 0 m to level 15 m . The force required to move the elevator at constant speed can be calculated as
Fc = (2000 kg) (9.81 m/s2)
= 19820 N
The power required to move the elevator between the levels in 20 s can be calculated as
P = (2000 kg) (9.81 m/s2) ((15 m) - (0 m)) / (20 s)
= 14865 W
= 14.9 kW