Stack or Flue Effect
The stack or flue effect occurs when the outdoor temperature is lower than indoor temperature.
The stack or flue effect occurs when the outdoor temperature is lower than the indoor temperature. The warm indoor air is lighter than cooler outside air.
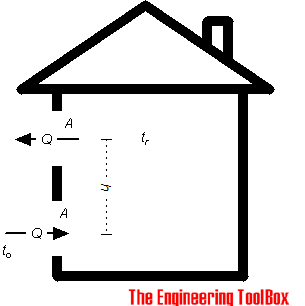
The air flow can be estimated as
Q = 9.4 A (h (tr - to))1/2 (1)
where
Q = rate of air flow (ft3/min)
A = free area of inlets and outlets - assumed equal (ft2)
h = height from inlets to outlets (ft)
tr = average room temperature at height h (oF)
to = outdoor temperature (oF)
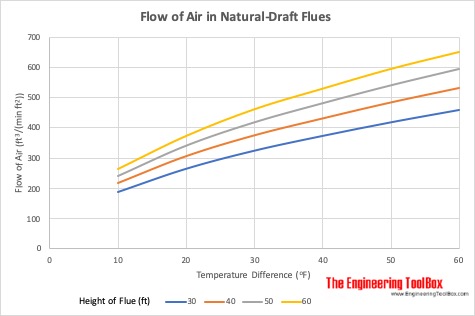
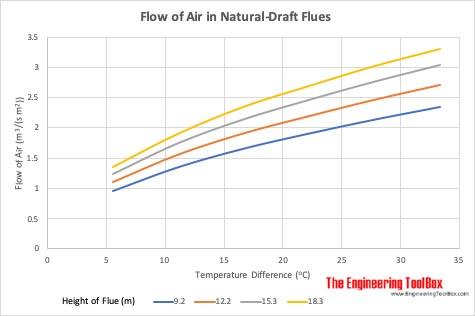
Flow of Air in Natural-Draft Flues