Sound Transmission through Duct Walls
Sound transmission from ducts to surrounding rooms.
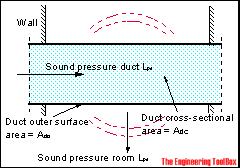
Sound or noise transmitted from the inside of a duct to the surrounding room can be expressed as:
Lp = LN - TL - 10 log(A F / 4 Ad) (1)
where
Lp = sound pressure in room (dB)
LN = sound power level in the duct (dB)
TL = transmission loss through duct wall (dB)
A = room absorption (m2 sabine)
F = cross section area of duct (m2)
Ad = surface area of duct (m2)
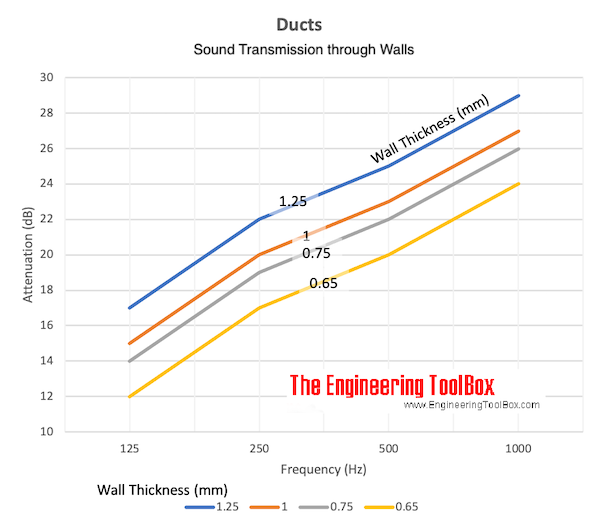
Typical sound transmission loss through duct walls are indicated in the table below:
| Duct sheet thickness (mm) | Frequency (Hz) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | |
| 1.25 | 17 | 22 | 25 | 29 |
| 1.0 | 15 | 20 | 23 | 27 |
| 0.75 | 14 | 19 | 22 | 26 |
| 0.65 | 12 | 17 | 20 | 24 |
The acoustic performance of round and oval ducts is superior to rectangular ducts since their curved surfaces allow less breakout noise. Low-frequency sound is better contained in round ducts.