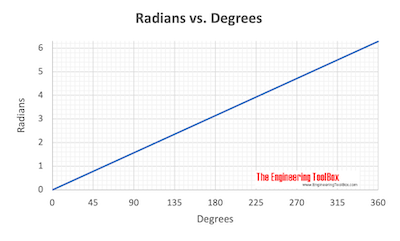
Radians vs. Degrees - Definition and Conversions
Radian is the SI unit of angle. Convert between degrees and radians. Calculate angular velocity.
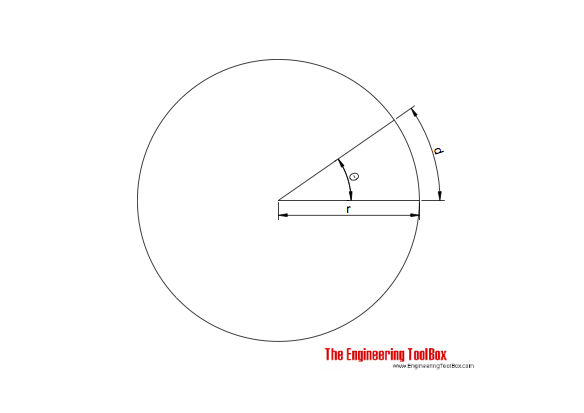
The radian is the SI derived unit of an angle where
θ = d / r (1)
where
θ = radian
d = circular distance measured along the arc (m, in)
r = radius in circle (m, in)
Since the length of a circle is 2 π r, and the radius of the circle is r - the radians in a complete circle can be calculated to
θ = 2 π r / r
= 2 π
=~ 6.283185
One radian can be expressed in degrees as
1 rad = 360o/ (2 π) = ~ 57.29578o (2a)
One radian can be expressed in revolutions as
1 rev = 1 / (2 π) = ~ 0.16 (2b)
One degree can be expressed in radians as
1o = 2 π / 360o = ~ 0.01745 radian (2c)
Note! - radians are used by default in angular expressions in most computer languages.
The radian is defined as the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc of circumference equal in length to the radius of the circle.
| degrees | 0o | 15o | 30o | 45o | 60o | 75o | 90o | 180o | 270o | 360o |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| radians | 0 | π/12 | π/6 | π/4 | π/3 | 5π/12 | π/2 | π | 3π/2 | 2π |
| 0 | 0.26 | 0.52 | 0.79 | 1.05 | 1.31 | 1.57 | 3.14 | 4.71 | 6.28 |
Radians to Degrees Converter
Degrees to Radians Converter
Angular Velocity
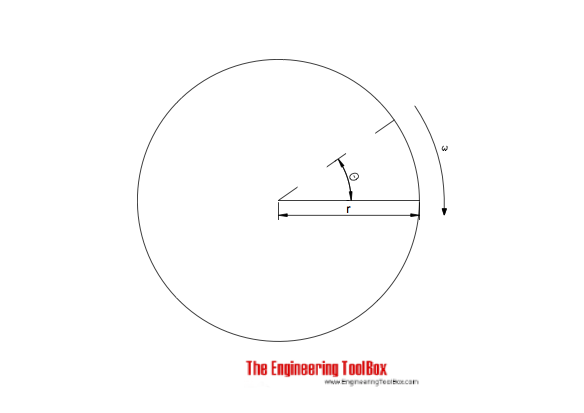
Converting angular velocity (ω) to other units
- ω = 1 rad/s = 9.55 r/min (rpm) = 0.159 r/s (rps) (3)
RPM to Radians and Degrees per Second Converter
| Revolutions (rpm) | Angular Velocity | |
|---|---|---|
| (rad/s) | (deg/s) | |
| 0 | 0.0 | 0 |
| 10 | 1.0 | 60 |
| 20 | 2.1 | 120 |
| 30 | 3.1 | 180 |
| 40 | 4.2 | 240 |
| 50 | 5.2 | 300 |
| 60 | 6.3 | 360 |
| 70 | 7.3 | 420 |
| 80 | 8.4 | 480 |
| 90 | 9.4 | 540 |
| 100 | 10.5 | 600 |
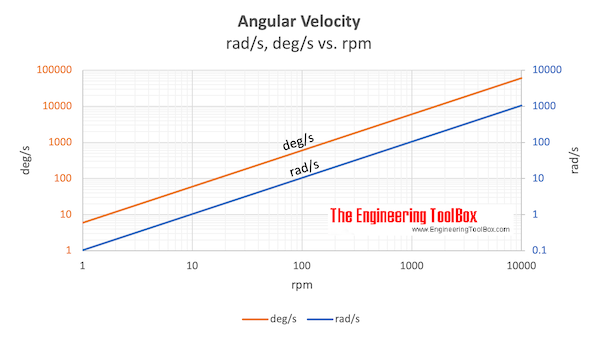
Download and print Angular Velocity chart
Example - Angular velocity 100 rad/s
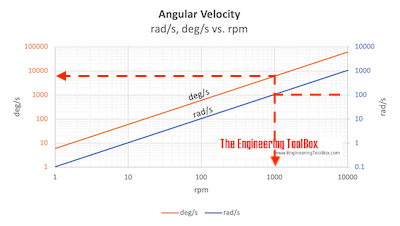
An angular velocity of 100 rad/s can as indicated in the chart above be estimated to aprox. 950 rpm and 5700 deg/s .
Related Searches
radians • radian definition • radian to degree conversion • degrees to radians • angular measurement • engineering mathematics • unit circle • trigonometry • angle conversion • pi • 360 •



