Pipe vs. Tube
Pipes and tubes are not exactly the same
Pipes
The purpose with a pipe is the transport of a fluid like water, oil or similar, and the most import property is the capacity or the inside diameter.
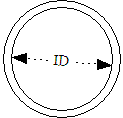
For a ASME/ANSI B 36.10 Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe the inside diameter - ID - of a NPS 2 inches pipe with
- schedule 40 is 2.067"
- schedule 80 is 1.939"
The inside diameters are close to 2" and the nominal diameter is related to the inside diameter. Outside diameter are 2.375" for both schedules.
Since the outside diameter of a single nominal pipe size is kept constant the inside diameter of a pipe depends on the "schedule" - or the thickness - of the pipe. The schedule and actual thickness of a pipe varies with size of the pipe.
Example - the thickness of a 2" schedule 40 pipe is 0.154" and the thickness of a 6" schedule 40 pipe is 0.280".
It is common to identify pipes in inches by using NPS or "Nominal Pipe Size". The metric equivalent is called DN or "diametre nominel". The metric designations conform to International Standards Organization (ISO) usage and apply to all plumbing, natural gas, heating oil, and in addition to miscellaneous piping used in buildings. Note - the use of NPS does not conform to American Standard pipe designations where the term NPS means "National Pipe Thread Straight".
Nominal Bore (NB) may be specified under British standards classifications along with schedule or wall thickness.
The tolerances are looser to pipes compared with tubes and pipes are often less expensive to produce than tubes.
Tubes
The nominal dimensions of tubes are based on the outside diameter. If we look at Copper Tubes - ASTM B88 the outside diameter of a 2" pipe is 2.125", relatively close to 2".
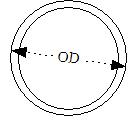
The inside diameter of a tube depends on the thickness of the tube. The thickness is often specified as gauge. If we look at Copper Tubes - ASTM B88 the wall thickness of 0.083"of a 2" pipe is gauge 14.
Tolerances are commonly higher with tubes compared to pipes and tubes are often more expensive to produce than pipes.



