Intermittent Combustion and Boiler Efficiency
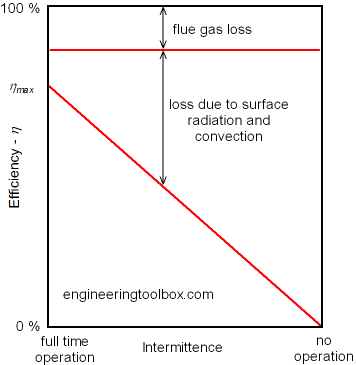
Efficiency reduction due to intermittent boiler operation.
Boiler combustion efficiency is reduced by intermittent operation due to
- the energy loss in the flue gas - either by unburned fuel with the excess of fuel or by heating more air than necessary with the excess of air
- the radiation and convection loss from the exterior surface of the boiler
Energy loss due to radiation and convection increases with intermittent operation and reduced combustion time as indicated in the diagram below: