Horsepower required to Compress Air
Calculate horsepower required by air compressors.
The horsepower required to adiabatic compression of air can be calculated with the calculator below:
Theoretical horsepower required to compress one cubic foot of free air (atmospheric pressure) for single-staged, two-staged and three-staged compressors are indicated in the diagram below. In general - plus 15-20% friction.
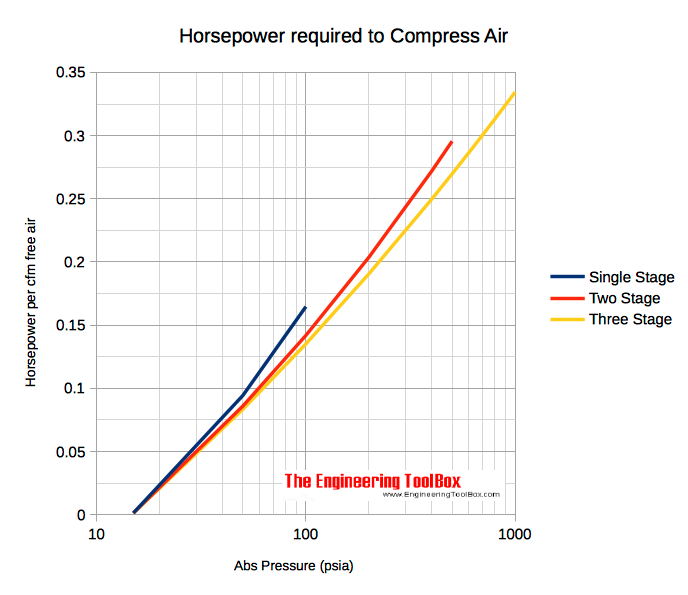
- 1 cfm (ft3/min) = 1.7 m3/h = 0.47 l/s = 28.3 l/min
- 1 psi (lb/in2) = 6894.8 Pa (N/m2) = 6.895×10-2 bar
- 1 hp = 745.7 W
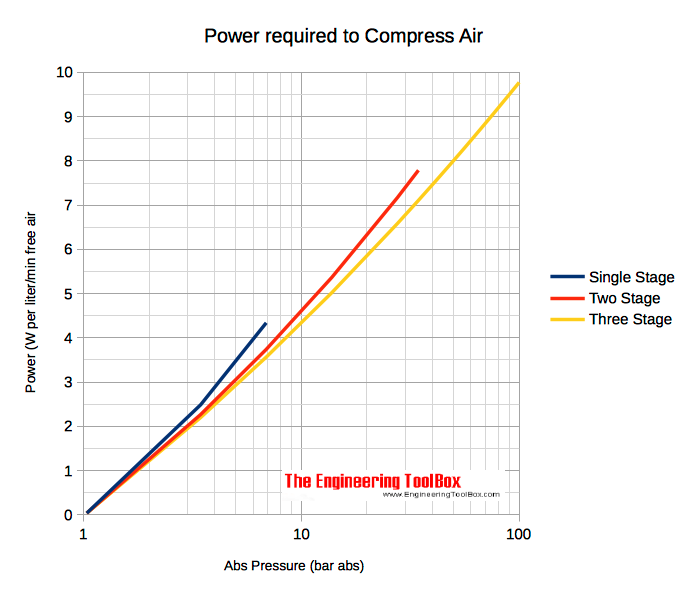
The power required for adiabatic (process without transfer of heat) compression of air can be expressed as
HP = (144 N P1 V k / (33000 (k - 1))) ((P2 / P1)(k - 1) / (N k) - 1) (1)
where
HP = horsepower
N = number of compression stages
k = 1.41 = adiabatic expansion coefficient
P1 = absolute initial atmospheric pressure (psi) (14.7 psi at sea level)
P2= absolute final pressure after compression (psi)
V = volume of air at atmospheric pressure - standard or free air (scfm, ft3/min)
- adiabatic compression (or expansion) takes place without transmission of heat



