Coulomb's Law
The electric force acting on a point charge.
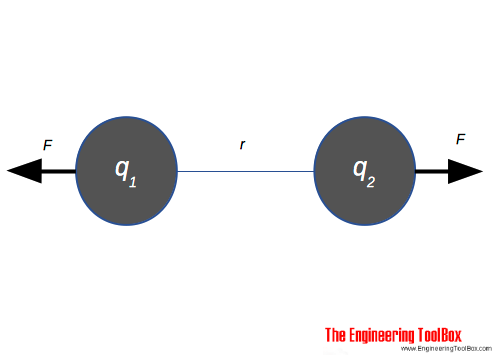
Coulomb's law calculates the electric force acting between to electric charges q1 and q 2and can be expressed as
F = k q1 q2 / r2
= q1 q2 / (4 π ε0 r2) (1)
where
F = force of attraction or repulsion (N)
k = Coulomb's constant = 1 / (4 π ε0) = 8.9875517873681764×109 (Nm2/C2) in air
q = charge (Coulombs, C)
r = distance between charges (m)
ε0 = permittivity of space or vacuum
The quantity of charge (number of electrons) is measured in the unit Coulomb - C - where
1 coulomb (C) = 6.24×1018 electrons
The smallest charge that exists is the charge carried by an electron equal to -1.602×10-19 coulomb.
Example - Force between two Charged Bodies
Two spheres in air with distance 20 mm is both charged with 2 μC (2×10-6 C) . The force acting between the two spheres can be calculated as
F = (8.98755×109 Nm2/C2) ((2 μC) (10-6 C/ μC)) ((2 μC) (10-6 C/ μC)) / ((20 mm)(10-3 m/mm))2
= 90 N



