Hydrocarbons - Melting Point vs. Molecular Weight
Calculate melting point of hydrocarbons from molecular weight (molar mass).
For pure compounds the following definitions can be given:
- Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid
- Freezing point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a solid
- The melting and freezing point change with pressure, but normally they are given at 1 atm.
- A pure substance has the same freezing and melting point (in practice a small difference between these quantities can be observed).
- For mixtures of compounds (as petroleum), there are ranges of melting and freezing points versus percent of the mixture melted or frozen.
- For a mixture, the initial melting point is close to the melting point of the lightest compound in the mixture, while the initial freezing point is close to the freezing point (or melting point) of the heaviest compound in the mixture.
- Since the melting point increases with molecular weight, for petroleum mixtures the initial freezing point is greater than the initial melting point.
Melting point is mainly a parameter that is needed for predicting solid-liquid phase behavior, especially for waxy oils. Equations developed by Riazi and Sahhaf for various homologous hydrocarbon groups can be used to estimate melting or freezing point of pure hydrocarbons with good accuracy (error of 1-1.5%) for practical calculations:

where
T MP = Melting point of n-alkanes (paraffins) in the carbon ranges of C5 - C 40 , in Kelvin [K]
T MCP = Melting point of n-alkycyclopentanes (naphthenes) in the carbon ranges of C 7 - C 41 , in Kelvin [K]
T MCH = Melting point of n-alkycyclohexanes (naphthenes) in the carbon ranges of C 7 - C 20 , in Kelvin [K]
T MA = Melting point of n-alkybenzenes (aromatics) in the carbon ranges of C 9 - C 42 , in Kelvin [K]
M = molecular weight (molar mass) of the actual substance [g/mol], [kg/kmol]
In fact, in wax precipitation linear hydrocarbons from C1 to C 15 as well as aromatics are absent, therefore there is no need for the melting point of very light hydrocarbons. For mixtures of hydrocarbons, the average molecular weight can be used in the equations, and then the melting temperature must be considered as the average melting temperature of the mixture.
See also Physical data for hydrocarbons , Physical data for alcohols and carboxylic acids , Melting points of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids , Physical data for organic nitrogen compounds , Physical data for organic sulfur compounds and Melting and Boiling Point, Density and Solubility in Water for Inorganic Compounds
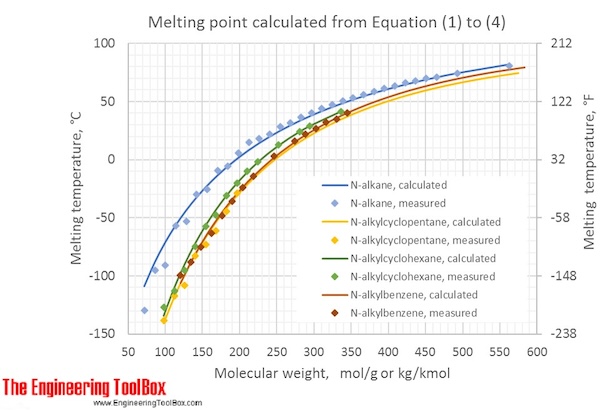
The figure shows calculated melting points (°C and °F) for the different kinds of hydrocarbons at varying molecular weights, compared to measured values:
Example 1: Melting point of nonylcyclopentane, with bruttoformula C 14 H 28
![]()
The molecular weight of nonylcyclopentane is: M = 14*12.02[g/mol] + 28*1.008[g/mol] = 196.4[g/mol]
For a cyclopentane like this, equation (2) is used: T M (heptylcyclopentane) = 370 - exp(6.52504 - 0.04945*196.4 (2/3) ) = 242.1[K]
Converted to °C and °F : 242.1[K] - 273.2 = -31.1[°C] and -31.1[°C]*1.8 + 32 = -23.9[°F]
Listed, measured values of melting point of nonylcyclopentane is -29°C.
Example 2: Melting and freezing point of a hydrocarbon mixture
A wax consists of 65wt% n-alkanes with an average molweight of 420 g/mol, 10wt% alkanecyclopentanes with an average molweight of 405 g/mol and 25wt% alkanecyclohexanes with an average molweight of 430 g/mol. What will the melting and freezing point of this wax be?
First, the average melting/freezing point of each hydrocarbon group is calculated:
T M (n-alkanes) = 397 - exp(6.5096 - 0.14187*420 0.47 ) = 337.6[K] = 65[°C]
T M (alkanecycklopentanes) = 370 - exp(6.52504 - 0.04945*405 2/3 ) = 324.7[K] = 51[°C]
T M (alkanecyclohexanes) = 360 - exp(6.55942 - 0.04681*430 0.7 ) = 333 [K] = 60[°C]
Note: The average molecular weight of 430 g/mol corresponds to a carbon number of 29, and thus, it is outside the validity range of Eq.(3). However, it is not expected to give large errors.
Since this is a mixture of compounds, and the average melting/freezing point is calculated from average molecular weights, the real melting and freezing will occur over a temperature range.
The solid wax will start to melt somewhat below 51 °C during heating, and the liquid wax will start to freeze somewhat above 65 °C during cooling. How far from the given temperatures it melts or freezes will depend on the width of the molecular weight range of the wax.
Related Topics
-
Material Properties
Properties of gases, fluids and solids. Densities, specific heats, viscosities and more. -
Melting and Freezing Points
Melting and freezing points of elements and chemical species at varying conditions.
Related Documents
-
Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids - Physical Data
Molweight, melting and boiling point, density, pKa-values, as well as number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in molecules are given for 150 different alcohols and acids. -
Hydrocarbon Mixtures - Average Boiling Points vs. Gravity and Molecular Weights
Formulas and examples of calculation of boiling point of hydrocarbon mixtures from gravity and molecular weight. -
Hydrocarbon Mixtures - Molecular Weight vs. Gravity and Average Boiling Point
Formulas and examples of calculation of average molecular weight of hydrocarbon mixtures from gravity and average boiling point, achieved from distillation data. -
Hydrocarbons - Physical Data
Molweight, melting and boiling point, density, flash point and autoignition temperature, as well as number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in each molecule for 200 different hydrocarbons. -
Inorganic Compounds in Water - Melting and Boiling Temperature, Density and Solubility
Physical constants for more than 280 common inorganic compounds. Density is given for the actual state at 25°C and for liquid phase at melting point temperature. -
Melting points of Hydrocarbons, Alcohols and Acids
Melting temperature (°C and °F) with carbon number up to C33. -
Mole and the Avagadro's Number
The mole is the SI base unit for an amount of a substance. -
Molecular Weight of Substances
Definition and molecular weight (molar mass) of some common substances. -
Naming of Organic Compounds
Nomenclature rules for different groups of organic compounds and functional groups, together with examples of use of the rules. -
Organic Nitrogen Compounds - Physical Data
Boiling and melting points of amines, diamines, pyrroles, pyridines, piperidines and quinolines shown together with their molecular structures, as well as molweights and density. -
Organic Sulfur Compounds - Physical Data
Boiling and melting points of thoils, sulfides, disulfides and thiophenes shown together with molecular structures, as well as molweights and density. -
Petroleum Products - Average Boiling Points
Definition, explanation and examples of calculation of various types of average boiling point of petroleum products and other mixtures of hydrocarbons: VABP, MABP, WABP, CABP and MeABP.




